News
EPJ Web of Conferences Highlight – XLVI Symposium on Nuclear Physics 2025
- Details
- Published on 05 August 2025
The XLVI Symposium on Nuclear Physics (SNP) took place in Cocoyoc, Mexico from January 6-9, 2025 with an attendance of about 90 participants from 15 different countries.
The SNP meeting has been organized every year since its beginning in 1978 with the exception of the COVID years, 2021 and 2022.
EPJ D Roadmap - Roadmap on carbon molecular nanostructures in space
- Details
- Published on 05 August 2025
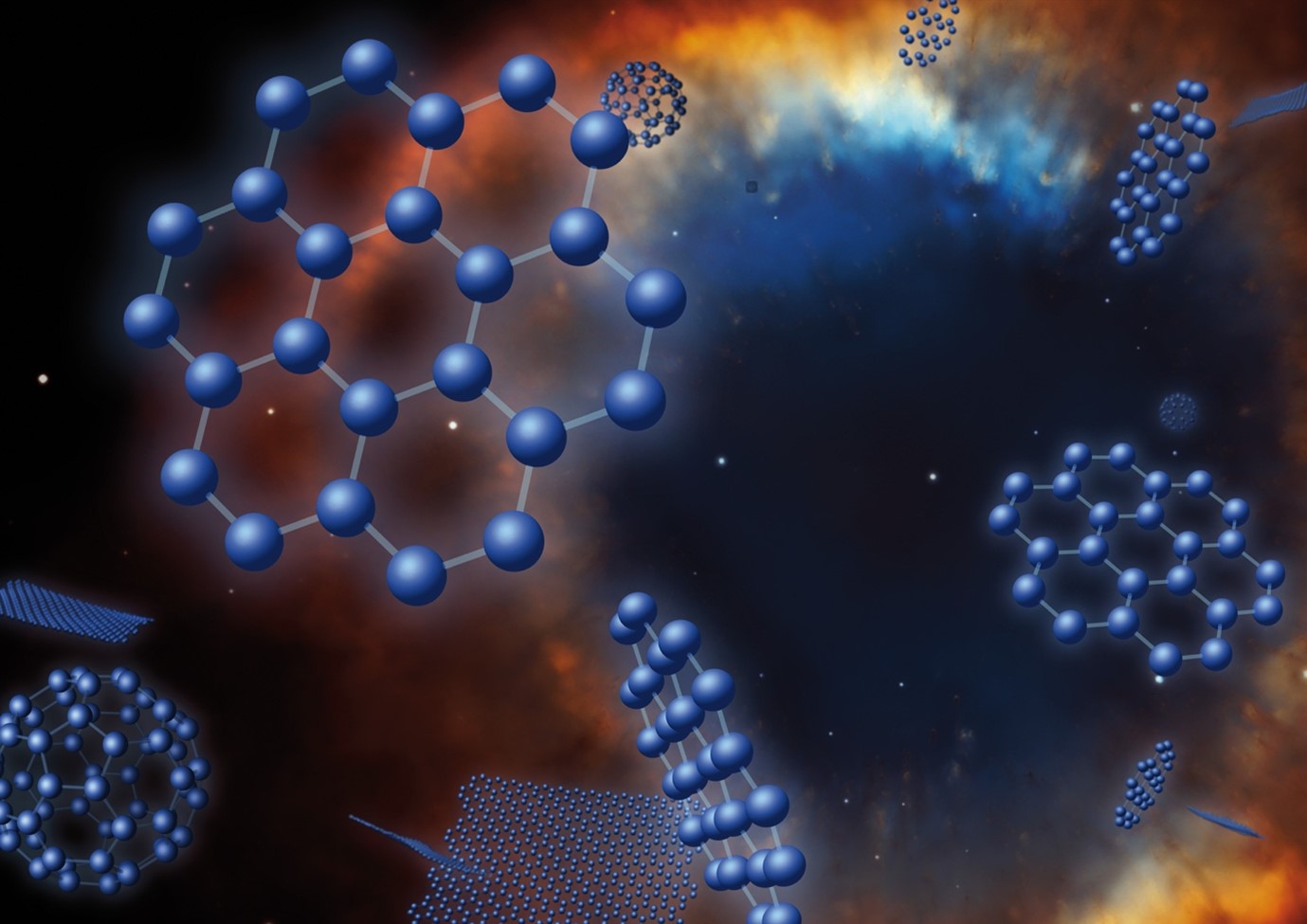
A new Roadmap is published in EPJD
The roadmap on carbon molecular nanostructures in space contains forty contributions from leading scientists in observational astronomy, laboratory astrophysics/chemistry, spectroscopy, theoretical chemistry, astrobiology, molecular reaction dynamics, graph theory and materials science. It highlights a rapidly developing, interdisciplinary field of research that is benefiting from recent technical advances in both observational astronomy and laboratory infrastructure combined with new powerful machine learning approaches to data analysis and modelling. The rapidly expanding inventory of carbon molecular nanostructures found in space is opening up many fundamental questions concerning their origin, astrochemical relevance and significance for the origin of life. The roadmap documents the state-of-the-art in observational and laboratory studies along with the current theoretical and experimental challenges to be overcome in order to achieve a greater understanding of the physics and chemistry of cosmic carbon molecular nanostructures. New insights are being made into the properties and resilience of these fascinating molecular species that are not only of fundamental importance for understanding the chemistry of space but have wider terrestrial relevance and impact in nanotechnology and catalysis.
EPJ E Highlight - Acanthamoeba castellanii offers a simplified model for density-driven cell migration
- Details
- Published on 24 July 2025
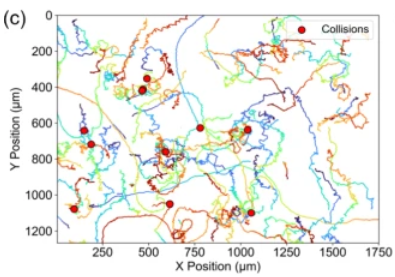
New analysis reveals that the motion of this unicellular amoeba is governed solely by cell–cell collisions, providing a useful model for isolating the effects of density on migration
Cell migration is vital to numerous biological processes. While often guided by long-range biochemical cues, it can also be influenced by direct physical collisions, which trigger biochemical signals within the affected cells. When studying this behaviour, it is important for researchers to consider how individual cell motions are affected by overall cell density. However, experiments have been complicated by the many interacting factors involved, making it difficult to isolate the specific impact of direct cell–cell collisions.
In new research published in EPJ E, a team led by Jean-Paul Rieu at Claude Bernard University Lyon 1 demonstrates how one unicellular amoeba species, Acanthamoeba castellanii (Ac), migrates in ways that are unaffected by long-range biochemical signalling – making it a promising model for studying how density influences cell migration. By using Ac, the researchers aim to gain deeper insights into the mechanisms of cell motion relevant to diverse biological processes, including immune responses, cancer cell invasion, and tissue development.
EPJ ST Highlight - Functional brain networks disrupted in major depression
- Details
- Published on 23 July 2025
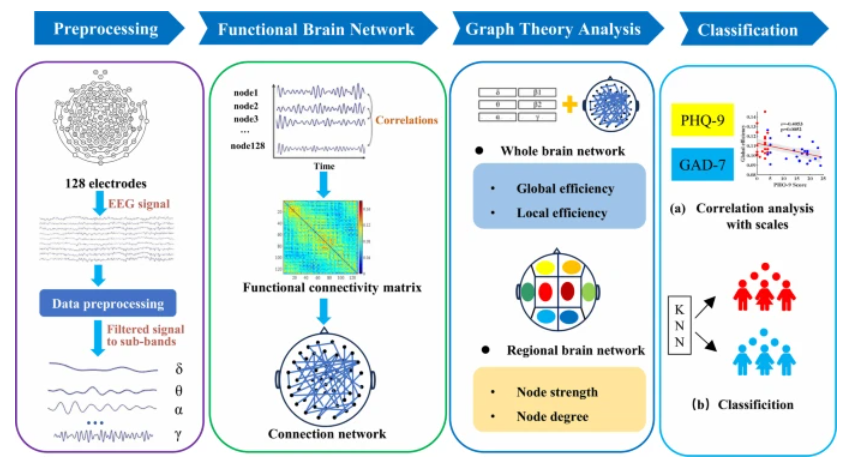
A detailed analysis of functional brain networks from individuals with and without major depressive disorder using graph theory has revealed subtle but significant differences between these groups that could aid early diagnosis of this devastating condition.
Severe depression or major depressive disorder (MDD) is the commonest serious mental disorder, and its high and growing prevalence – it is thought to affect over 300 million people worldwide – represents a major societal challenge. Many studies have shown some characteristic patterns in brain structure and activity in depressed individuals, but the details and the likely reasons are unknown. Now, however, an interdisciplinary group of researchers led by Mengmeng Du of Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, China, have used the mathematical technique of graph theory to analyse networks of brain activity in different regions and at different scales. This work has been published in the journal EPJ Special Topics (EPJ ST).
EPJ Plus Focus Point Issue: Accelerator-based Photon Science Strategy, Prospects and Roadmap in Europe
- Details
- Published on 23 July 2025

Guest Editors: Rafael Abela, Thomas Tschentscher, Jean Susini, Gastón García
The League of European Accelerator-based Photon Sources (LEAPS) is an alliance of all synchrotron and free electron laser user facilities in Europe. These facilities are an essential element of the scientific landscape in Europe and elsewhere, undergoing fast and profound changes of great relevance for the scientific community and with a substantial societal impact. This focus point issue features the current status and future scientific strategy of LEAPS. The collection includes papers about most of the LEAPS members, along with two specific papers on the LEAPS general strategy and the critical aspect of data.
All articles are available here and are freely accessible until 22 September 2025. For further information, read this highlight.
EPJ ST: Nuggehalli M. Ravindra new Editor on board
- Details
- Published on 17 July 2025

The publishers are very pleased to announce that Dr. Nuggehalli M. Ravindra (Ravi) has recently joined the EPJST Editorial Board.
N M Ravindra (Ravi) is Professor of Physics at the New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT). He was the Chair of the Physics Department (2009-13) and Director, Interdisciplinary Program in Materials Science and Engineering at NJIT (2009-2016). Ravi is the Founding Editor of Emerging Materials Research. He has been a frequent Guest Editor of several journals including JEM, the Journal of Electronic Materials; JOM, Polymers for Advanced Technologies and MDPI Journals. Before joining NJIT in 1987, Ravi had been associated with Vanderbilt University, the Microelectronics Center of North Carolina (MCNC), North Carolina State University, Abdus Salam Center for Theoretical Physics (formerly ICTP, Trieste), Politecnico di Torino, CNRS associated labs in Paris and Montpellier. Ravi holds a PhD in Physics from Indian Institute of Technology (Roorkee, India), MS & BS in Physics from Bangalore University, India. Ravi and his research team have published over 350 papers in international journals, books and conference proceedings and 8 Books; his team has three issued patents; he has organized over 40 international conferences; and he has given over 80 talks in international meetings.
Ravi's research interests include devices, education, energy storage, materials, manufacturing, optical coatings, renewable energy, semiconductors and sensors.
EPJ B Highlight - Uncovering the magnetic responses of anisotropic semimetals
- Details
- Published on 14 July 2025

Calculations show that magnetic fields can alter the responses of anisotropic 2D semimetals to electric fields and temperature gradients – but only when applied perpendicular to the material’s plane
For solid-state physicists, graphene has become a posterchild of 2D semimetals: materials whose electronic structures fall between those of a metal and a semiconductor. Owing to the honeycomb structure of its carbon atoms, graphene hosts an orderly arrangement of Dirac cones – pairs of opposite-facing, cone-shaped energy bands that touch at a single point. Immediately surrounding such a point, electron energy varies linearly with momentum, just like for massless particles such as photons – leading to exotic and often useful electronic properties.
Through a new paper published in EPJ B, Ipsita Mandal at the Shiv Nadar Institution of Eminence, India, presents fresh calculations of how these properties vary in the presence of magnetic fields, particularly when 2D semimetals are structurally distorted. Her results show that these materials’ electrical and thermal responses are affected only when the magnetic field is oriented perpendicular to the 2D plane. This finding offers deeper insight into the electronic behaviour of semimetals – potentially broadening their already wide range of technological applications.
EPJ Plus Highlight - Hybrid algorithm uncovers robust scar states for quantum computing
- Details
- Published on 14 July 2025
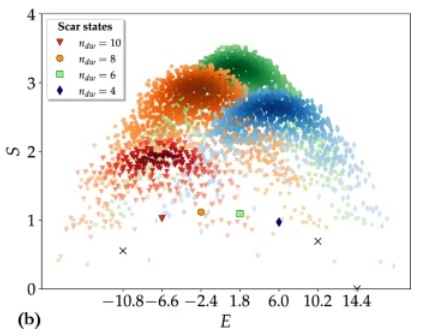
An algorithm that merges classical and quantum computing resources could help reveal robust quantum states hidden within chaotic, noisy systems
Since today’s quantum computing architectures are inherently noisy, they still struggle to generate large amounts of entanglement between qubits. One promising solution could be to target quantum scar states, which can emerge in complex, many-body systems. These states are unusually simple compared with their chaotic surroundings, and they may offer a more robust way to store quantum information – making them especially attractive for building stable quantum logic gates.
Through new research published in EPJ Plus, an international team led by Gabriele Cenedese at the University of Insubria, Italy, demonstrates how the limited entanglement in noisy quantum computers could be transformed into an advantage, making it easier to identify scar states within chaotic quantum systems. Involving a specialised hybrid algorithm, the team’s approach could help pave the way toward more scalable quantum architectures – reducing the need for complex and costly error-correction techniques.
EPJ ST Highlight - Data-Driven Insights into Inkjet Droplet Formation
- Details
- Published on 09 July 2025

High-speed image analysis shows how the control parameters of inkjet printers are linked to the shapes of the ink droplets they produce – helping researchers to optimise the printing process.
Inkjet printing has become a cornerstone of high-tech microfabrication, underpinning applications ranging from microchip production and drug delivery to DNA sequencing and tissue engineering. In these fields, precision is paramount - the ability to reliably place picolitre-sized droplets with exact morphology determines the success of both medical treatments and microelectronic device fabrication.
Despite advances in computational fluid dynamics (CFD), simulating and controlling droplet formation in real-world conditions remains a challenge due to the complexity of two-phase flows and the vast number of operational parameters involved. To address this, researchers are turning to data-driven approaches as a complementary or alternative strategy. These methods can reduce reliance on time-consuming simulations and enable real-time analysis and decision-making in manufacturing environments.
In a new study published in EPJ Special Topics (EPJ ST), researchers at CIMNE/UPC present a comprehensive data-driven investigation of droplet morphology in inkjet printing. The team, led by Pavel Ryzhakov, began by performing extensive controlled droplet-generation experiments using a piezoelectric inkjet dispenser. Each droplet was captured via high-speed imaging, yielding a rich dataset of raw images and extracted geometrical features.
EPJ B Highlight - Understanding 2D Dirac semimetals in tilted magnetic fields
- Details
- Published on 09 July 2025

Model reveals that within ultrathin Dirac semimetal films, the transport of quantised Dirac fermions can occur in two distinct ways, depending on how the film is tilted relative to an applied magnetic field
Dirac matter is an exotic phase of matter in which quasiparticles – arising from low-energy electron excitations behave like relativistic particles – obey the rules of both quantum mechanics and special relativity. Among these systems are materials called Dirac semimetals, which are characterised by discrete points where their conduction and valence bands touch, forming a linear energy–momentum relationship. Today, physicists are especially interested in the unusual topological phases that can emerge when Dirac semimetals are fabricated into ultrathin 2D films.
Through theoretical analysis published in EPJ B, Rui Min and Yi-Xiang Wang at Jiangnan University, China, investigate how Dirac fermions are transported in thin semimetal films under tilted magnetic fields. Their model reveals that the quantum Hall behaviour of these materials changes in distinct ways depending on the field’s orientation – offering new insights into the topological nature of Dirac matter. Their results could lead to applications in areas including quantum computing, low-power electronics, and spin-based information processing.




