https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-025-14396-3
Regular Article - Experimental Physics
Ion transport on phased radiofrequency carpets in xenon gas
1
Department of Physics, University of Texas at Arlington, 76019, Arlington, TX, USA
2
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Notre Dame, 46556, Notre Dame, IN, USA
3
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Texas at Arlington, 76019, Arlington, TX, USA
4
Argonne National Laboratory, 60439, Argonne, IL, USA
5
Department of Physics and Astronomy, Manchester University, M13 9PL, Manchester, UK
6
Instituto de Instrumentación para Imagen Molecular (I3M), Centro Mixto CSIC-Universitat Politècnica de València, Camino de Vera s/n, 46022, Valencia, Spain
7
Department of Organic Chemistry I, Universidad del Pais Vasco (UPV/EHU), Centro de Innovación en Química Avanzada (ORFEO-CINQA), 20018, San Sebastián/Donostia, Spain
8
Donostia International Physics Center, BERC Basque Excellence Research Centre, Manuel de Lardizabal 4, 20018, San Sebastián/Donostia, Spain
9
Unit of Nuclear Engineering, Faculty of Engineering Sciences, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, P.O.B. 653, 8410501, Beersheba, Israel
10
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL), 99352, Richland, WA, USA
11
Instituto de Física Corpuscular (IFIC), CSIC and Universitat de València, Calle Catedrático José Beltrán, 2, 46980, Paterna, Spain
12
Institute of Nanostructures, Nanomodelling and Nanofabrication (i3N), Universidade de Aveiro, Campus de Santiago, 3810-193, Aveiro, Portugal
13
Department of Physics, Universidad del Pais Vasco (UPV/EHU), PO Box 644, 48080, Bilbao, Spain
14
Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc, Paseo de los Ayerbe s/n, 22880, Canfranc Estación, Spain
15
LIP, Department of Physics, University of Coimbra, 3004-516, Coimbra, Portugal
16
Centro de Física de Materiales (CFM), CSIC and Universidad del Pais Vasco (UPV/EHU), Manuel de Lardizabal 5, 20018, San Sebastián/Donostia, Spain
17
Department of Physics, Harvard University, 02138, Cambridge, MA, USA
18
Department of Applied Chemistry, Universidad del Pais Vasco (UPV/EHU), Manuel de Lardizabal 3, 20018, San Sebastián/Donostia, Spain
19
Instituto Gallego de Física de Altas Energías, Univ. de Santiago de Compostela, Campus sur, Rúa Xosé María Suárez Núñez, s/n, 15782, Santiago de Compostela, Spain
20
LIBPhys, Physics Department, University of Coimbra, Rua Larga, 3004-516, Coimbra, Portugal
21
Ikerbasque (Basque Foundation for Science), 48009, Bilbao, Spain
22
Department of Physics and Astronomy, Iowa State University, 50011-3160, Ames, IA, USA
23
Racah Institute of Physics, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, 9190401, Jerusalem, Israel
24
Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, 60510, Batavia, IL, USA
25
Escola Politècnica Superior, Universitat de Girona, Av. Montilivi, s/n, 17071, Girona, Spain
26
Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel
27
University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, USA
28
Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, USA
Received:
20
February
2025
Accepted:
4
June
2025
Published online:
23
June
2025
We present the design and performance of a four-phased radiofrequency (RF) carpet system for ion transport between 200–600 mbar, significantly higher than previously demonstrated RF carpet applications. The RF carpet, designed with a 160 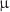 m pitch, is applied to the lateral collection of ions in xenon at pressures up to 600 mbar. We demonstrate transport efficiency of caesium ions across varying pressures, and compare with microscopic simulations made in the SIMION package. The novel use of an N-phased RF carpet can achieve ion levitation and controlled lateral motion in a denser environment than is typical for RF ion transport in gases. This feature makes such carpets strong candidates for ion transport to single ion sensors envisaged for future neutrinoless double-beta decay experiments in xenon gas.
m pitch, is applied to the lateral collection of ions in xenon at pressures up to 600 mbar. We demonstrate transport efficiency of caesium ions across varying pressures, and compare with microscopic simulations made in the SIMION package. The novel use of an N-phased RF carpet can achieve ion levitation and controlled lateral motion in a denser environment than is typical for RF ion transport in gases. This feature makes such carpets strong candidates for ion transport to single ion sensors envisaged for future neutrinoless double-beta decay experiments in xenon gas.
© The Author(s) 2025
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




