https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-025-14315-6
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
A joint analysis of strong lensing and type Ia supernovae to determine the Hubble constant
1
Departamento de Física Teórica e Experimental, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, 59300-000, Natal, RN, Brazil
2
Departamento de Física, Universidade Federal de Campina Grande, 58429-900, Campina Grande, PB, Brazil
Received:
21
March
2025
Accepted:
14
May
2025
Published online:
26
May
2025
We present a cosmological model-independent determination of the Hubble constant, 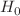 , by combining time-delay measurements from seven TDCOSMO systems, Einstein radius measurements, and type Ia supernovae data sourced from the Pantheon+ sample. For each lens of time-delay system, we calculate the angular diameter distance
, by combining time-delay measurements from seven TDCOSMO systems, Einstein radius measurements, and type Ia supernovae data sourced from the Pantheon+ sample. For each lens of time-delay system, we calculate the angular diameter distance 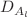 using the product
using the product 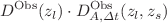 , where
, where  is reconstructed via Gaussian Processes from 99 Einstein radius measurements, and
is reconstructed via Gaussian Processes from 99 Einstein radius measurements, and 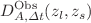 is the time-delay angular distance. We also reconstruct the unanchored luminosity distance
is the time-delay angular distance. We also reconstruct the unanchored luminosity distance 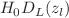 from supernova data. By using the cosmic distance duality relation validity, we anchor
from supernova data. By using the cosmic distance duality relation validity, we anchor 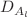 and
and 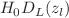 to infer
to infer 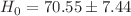 km/s/Mpc (68% CL). Our result, though not resolving the Hubble tension, offers a cosmological model-independent consistency check and highlights the potential of using strong lensing and supernovae data via the cosmic distance duality relation to constrain
km/s/Mpc (68% CL). Our result, though not resolving the Hubble tension, offers a cosmological model-independent consistency check and highlights the potential of using strong lensing and supernovae data via the cosmic distance duality relation to constrain 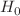 .
.
© The Author(s) 2025
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




