https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-025-14070-8
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Universal thermodynamic topological classes of black holes in a perfect fluid dark matter background
1
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Engineering and Computing, National University of Modern Languages, 44000, Islamabad, Pakistan
2
Department of Mathematics, School of Natural Sciences, National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), 44000, Islamabad, Pakistan
3
Department of Basic Sciences and Humanities, College of Electrical and Mechanical Engineering, National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), 44000, Islamabad, Pakistan
Received:
10
January
2025
Accepted:
12
March
2025
Published online:
29
March
2025
In this paper, we study the universal thermodynamic topological classes of a family of black holes in a perfect fluid dark matter (PFDM) background. Recent research on black hole thermodynamics suggests that all black holes can be cast into four universal thermodynamic classes, denoted by 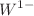 ,
, 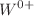 ,
, 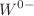 , and
, and  . Our study reveals that the Schwarzschild black hole in PFDM belongs to the
. Our study reveals that the Schwarzschild black hole in PFDM belongs to the 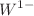 class, and the independence of black hole size is thermodynamically unstable in both the low- and high-temperature limits. The Reissner–Nordström, Kerr, and Kerr–Newman black holes in the PFDM background belong to the same universal thermodynamic class,
class, and the independence of black hole size is thermodynamically unstable in both the low- and high-temperature limits. The Reissner–Nordström, Kerr, and Kerr–Newman black holes in the PFDM background belong to the same universal thermodynamic class, 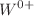 , which represents small-stable black holes and large-unstable black holes at low-temperature limits, whereas no black hole state exists at high temperatures. The AdS black holes behave differently when compared to their counterparts in PFDM. The Schwarzschild–AdS black hole belongs to the
, which represents small-stable black holes and large-unstable black holes at low-temperature limits, whereas no black hole state exists at high temperatures. The AdS black holes behave differently when compared to their counterparts in PFDM. The Schwarzschild–AdS black hole belongs to the 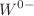 class, indicating that no black hole state exists at low temperatures, but small-unstable and large-stable black hole states exist at high temperatures. Furthermore, the Kerr–AdS black hole belongs to the
class, indicating that no black hole state exists at low temperatures, but small-unstable and large-stable black hole states exist at high temperatures. Furthermore, the Kerr–AdS black hole belongs to the  class, characterized by small-stable black holes at low temperatures, large-stable black holes at high temperatures, and unstable intermediate-sized black holes at both low and high temperatures. Thus, the presence of PFDM does not affect the stability of the black hole. These findings uncover the universal topological classifications underlying black hole thermodynamics, offering profound insights into the fundamental principles of quantum gravity.
class, characterized by small-stable black holes at low temperatures, large-stable black holes at high temperatures, and unstable intermediate-sized black holes at both low and high temperatures. Thus, the presence of PFDM does not affect the stability of the black hole. These findings uncover the universal topological classifications underlying black hole thermodynamics, offering profound insights into the fundamental principles of quantum gravity.
© The Author(s) 2025
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




