https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-025-13793-y
Regular Article - Experimental Physics
Common femtoscopic hadron-emission source in pp collisions at the LHC
1
A.I. Alikhanyan National Science Laboratory (Yerevan Physics Institute) Foundation, Yerevan, Armenia
2
AGH University of Krakow, Cracow, Poland
3
Bogolyubov Institute for Theoretical Physics, National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Kiev, Ukraine
4
Department of Physics and Centre for Astroparticle Physics and Space Science (CAPSS), Bose Institute, Kolkata, India
5
California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo, CA, USA
6
Central China Normal University, Wuhan, China
7
Centro de Aplicaciones Tecnológicas y Desarrollo Nuclear (CEADEN), Havana, Cuba
8
Centro de Investigación y de Estudios Avanzados (CINVESTAV), Mexico City and Mérida, Mexico
9
Chicago State University, Chicago, IL, USA
10
China Institute of Atomic Energy, Beijing, China
11
China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China
12
Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Republic of Korea
13
Faculty of Mathematics, Physics and Informatics, Comenius University Bratislava, Bratislava, Slovak Republic
14
COMSATS University Islamabad, Islamabad, Pakistan
15
Creighton University, Omaha, NE, USA
16
Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, India
17
Department of Physics, Pusan National University, Pusan, Republic of Korea
18
Department of Physics, Sejong University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
19
Department of Physics, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA
20
Department of Physics, University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway
21
Department of Physics and Technology, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway
22
Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Pavia, Pavia, Italy
23
Dipartimento di Fisica dell’Università and Sezione INFN, Cagliari, Italy
24
Dipartimento di Fisica dell’Università and Sezione INFN, Trieste, Italy
25
Dipartimento di Fisica dell’Università and Sezione INFN, Turin, Italy
26
Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia dell’Università and Sezione INFN, Bologna, Italy
27
Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia dell’Università and Sezione INFN, Catania, Italy
28
Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia dell’Università and Sezione INFN, Padua, Italy
29
Dipartimento di Fisica ‘E.R. Caianiello’ dell’Università and Gruppo Collegato INFN, Salerno, Italy
30
Dipartimento DISAT del Politecnico and Sezione INFN, Turin, Italy
31
Dipartimento di Scienze MIFT, Università di Messina, Messina, Italy
32
Dipartimento Interateneo di Fisica ‘M. Merlin’ and Sezione INFN, Bari, Italy
33
European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), Geneva, Switzerland
34
Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture, University of Split, Split, Croatia
35
Faculty of Engineering and Science, Western Norway University of Applied Sciences, Bergen, Norway
36
Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague, Prague, Czech Republic
37
Faculty of Physics, Sofia University, Sofia, Bulgaria
38
Faculty of Science, P.J. Šafárik University, Košice, Slovak Republic
39
Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies, Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität Frankfurt, Frankfurt, Germany
40
Fudan University, Shanghai, China
41
Gangneung-Wonju National University, Gangneung, Republic of Korea
42
Department of Physics, Gauhati University, Guwahati, India
43
Helmholtz-Institut für Strahlen- und Kernphysik, Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn, Bonn, Germany
44
Helsinki Institute of Physics (HIP), Helsinki, Finland
45
High Energy Physics Group, Universidad Autónoma de Puebla, Puebla, Mexico
46
Horia Hulubei National Institute of Physics and Nuclear Engineering, Bucharest, Romania
47
HUN-REN Wigner Research Centre for Physics, Budapest, Hungary
48
Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT), Mumbai, India
49
Indian Institute of Technology Indore, Indore, India
50
INFN, Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati, Frascati, Italy
51
INFN, Sezione di Bari, Bari, Italy
52
INFN, Sezione di Bologna, Bologna, Italy
53
INFN, Sezione di Cagliari, Cagliari, Italy
54
INFN, Sezione di Catania, Catania, Italy
55
INFN, Sezione di Padova, Padua, Italy
56
INFN, Sezione di Pavia, Pavia, Italy
57
INFN, Sezione di Torino, Turin, Italy
58
INFN, Sezione di Trieste, Trieste, Italy
59
Inha University, Incheon, Republic of Korea
60
Institute for Gravitational and Subatomic Physics (GRASP), Utrecht University/Nikhef, Utrecht, The Netherlands
61
Institute of Experimental Physics, Slovak Academy of Sciences, Košice, Slovak Republic
62
Institute of Physics, Homi Bhabha National Institute, Bhubaneswar, India
63
Institute of Physics of the Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, Czech Republic
64
Institute of Space Science (ISS), Bucharest, Romania
65
Institut für Kernphysik, Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität Frankfurt, Frankfurt, Germany
66
Instituto de Ciencias Nucleares, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Mexico City, Mexico
67
Instituto de Física, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul (UFRGS), Porto Alegre, Brazil
68
Instituto de Física, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Mexico City, Mexico
69
iThemba LABS, National Research Foundation, Somerset West, South Africa
70
Jeonbuk National University, Jeonju, Republic of Korea
71
Johann-Wolfgang-Goethe Universität Frankfurt Institut für Informatik, Fachbereich Informatik und Mathematik, Frankfurt, Germany
72
Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
73
KTO Karatay University, Konya, Turkey
74
Laboratoire de Physique Subatomique et de Cosmologie, Université Grenoble-Alpes, CNRS-IN2P3, Grenoble, France
75
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA, USA
76
Division of Particle Physics, Lund University Department of Physics, Lund, Sweden
77
Nagasaki Institute of Applied Science, Nagasaki, Japan
78
Nara Women’s University (NWU), Nara, Japan
79
Department of Physics, School of Science, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens, Greece
80
National Centre for Nuclear Research, Warsaw, Poland
81
National Institute of Science Education and Research, Homi Bhabha National Institute, Jatni, India
82
National Nuclear Research Center, Baku, Azerbaijan
83
National Research and Innovation Agency-BRIN, Jakarta, Indonesia
84
Niels Bohr Institute, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark
85
Nikhef, National Institute for Subatomic Physics, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
86
Nuclear Physics Group, STFC Daresbury Laboratory, Daresbury, UK
87
Nuclear Physics Institute of the Czech Academy of Sciences, Husinec-Řež, Czech Republic
88
Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN, USA
89
Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA
90
Physics Department, Faculty of Science, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia
91
Physics Department, Panjab University, Chandigarh, India
92
Physics Department, University of Jammu, Jammu, India
93
Physics Program and International Institute for Sustainability with Knotted Chiral Meta Matter (SKCM2), Hiroshima University, Hiroshima, Japan
94
Physikalisches Institut, Eberhard-Karls-Universität Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany
95
Physikalisches Institut, Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany
96
Physik Department, Technische Universität München, Munich, Germany
97
Politecnico di Bari and Sezione INFN, Bari, Italy
98
Research Division and ExtreMe Matter Institute EMMI, GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH, Darmstadt, Germany
99
Saga University, Saga, Japan
100
Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics, Homi Bhabha National Institute, Kolkata, India
101
School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK
102
Sección Física, Departamento de Ciencias, Pontificia Universidad Católica del Perú, Lima, Peru
103
Stefan Meyer Institut für Subatomare Physik (SMI), Vienna, Austria
104
SUBATECH, IMT Atlantique, Nantes Université, CNRS-IN2P3, Nantes, France
105
Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon City, Republic of Korea
106
Suranaree University of Technology, Nakhon Ratchasima, Thailand
107
Technical University of Košice, Košice, Slovak Republic
108
The Henryk Niewodniczanski Institute of Nuclear Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences, Cracow, Poland
109
The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, USA
110
Universidad Autónoma de Sinaloa, Culiacán, Mexico
111
Universidade de São Paulo (USP), São Paulo, Brazil
112
Universidade Estadual de Campinas (UNICAMP), Campinas, Brazil
113
Universidade Federal do ABC, Santo Andre, Brazil
114
Universitatea Nationala de Stiinta si Tehnologie Politehnica Bucuresti, Bucharest, Romania
115
University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa
116
University of Derby, Derby, UK
117
University of Houston, Houston, TX, USA
118
University of Jyväskylä, Jyväskylä, Finland
119
University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS, USA
120
University of Liverpool, Liverpool, UK
121
University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China
122
University of South-Eastern Norway, Kongsberg, Norway
123
University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, USA
124
University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa
125
University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
126
University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba, Japan
127
Universität Münster, Institut für Kernphysik, Münster, Germany
128
Université Clermont Auvergne, CNRS/IN2P3, LPC, Clermont-Ferrand, France
129
Université de Lyon, CNRS/IN2P3, Institut de Physique des 2 Infinis de Lyon, Lyon, France
130
Université de Strasbourg, CNRS, IPHC UMR 7178, F-67000 Strasbourg, France, Strasbourg, France
131
Université Paris-Saclay, Centre d’Etudes de Saclay (CEA), IRFU, Départment de Physique Nucléaire (DPhN), Saclay, France
132
Université Paris-Saclay, CNRS/IN2P3, IJCLab, Orsay, France
133
Università degli Studi di Foggia, Foggia, Italy
134
Università del Piemonte Orientale, Vercelli, Italy
135
Università di Brescia, Brescia, Italy
136
Variable Energy Cyclotron Centre, Homi Bhabha National Institute, Kolkata, India
137
Warsaw University of Technology, Warsaw, Poland
138
Wayne State University, Detroit, MI, USA
139
Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA
140
Yonsei University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
141
Zentrum für Technologie und Transfer (ZTT), Worms, Germany
142
Affiliated with an Institute Covered by a Cooperation Agreement with CERN, Geneva, Switzerland
143
Affiliated with an International Laboratory Covered by a Cooperation Agreement with CERN, Geneva, Switzerland
144
Max-Planck-Institut fur Physik, Munich, Germany
145
Italian National Agency for New Technologies, Energy and Sustainable Economic Development (ENEA), Bologna, Italy
146
Dipartimento DET del Politecnico di Torino, Turin, Italy
147
Yildiz Technical University, Istanbul, Turkey
148
Department of Applied Physics, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, India
149
Institute of Theoretical Physics, University of Wroclaw, Poland
150
An Institution Covered by a Cooperation Agreement with CERN, Geneva, Switzerland
151
CERN, 1211, Geneva 23, Switzerland
Received:
13
January
2024
Accepted:
21
May
2024
Published online:
19
February
2025
The femtoscopic study of pairs of identical pions is particularly suited to investigate the effective source function of particle emission, due to the resulting Bose–Einstein correlation signal. In small collision systems at the LHC, pp in particular, the majority of the pions are produced in resonance decays, which significantly affect the profile and size of the source. In this work, we explicitly model this effect in order to extract the primordial source in pp collisions at 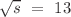 TeV from charged
TeV from charged  –
– correlations measured by ALICE. We demonstrate that the assumption of a Gaussian primordial source is compatible with the data and that the effective source, resulting from modifications due to resonances, is approximately exponential, as found in previous measurements at the LHC. The universality of hadron emission in pp collisions is further investigated by applying the same methodology to characterize the primordial source of
correlations measured by ALICE. We demonstrate that the assumption of a Gaussian primordial source is compatible with the data and that the effective source, resulting from modifications due to resonances, is approximately exponential, as found in previous measurements at the LHC. The universality of hadron emission in pp collisions is further investigated by applying the same methodology to characterize the primordial source of 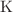 –
–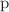 pairs. The size of the primordial source is evaluated as a function of the transverse mass (
pairs. The size of the primordial source is evaluated as a function of the transverse mass (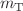 ) of the pairs, leading to the observation of a common scaling for both
) of the pairs, leading to the observation of a common scaling for both  –
– and
and 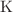 –
–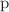 , suggesting a collective effect. Further, the present results are compatible with the
, suggesting a collective effect. Further, the present results are compatible with the 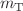 scaling of the
scaling of the 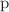 –
–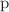 and p
and p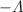 primordial source measured by ALICE in high multiplicity pp collisions, providing additional evidence for the presence of a common emission source for all hadrons in small collision systems at the LHC. This will allow the determination of the source function for any hadron–hadron pairs with high precision, granting access to the properties of the possible final-state interaction among pairs of less abundantly produced hadrons, such as strange or charmed particles.
primordial source measured by ALICE in high multiplicity pp collisions, providing additional evidence for the presence of a common emission source for all hadrons in small collision systems at the LHC. This will allow the determination of the source function for any hadron–hadron pairs with high precision, granting access to the properties of the possible final-state interaction among pairs of less abundantly produced hadrons, such as strange or charmed particles.
© The Author(s) 2025
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




