https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-023-12192-5
Regular Article - Experimental Physics
Impact of beam–beam effects on absolute luminosity calibrations at the CERN Large Hadron Collider
1
Tomsk Polytechnic University, Tomsk, Russia
2
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Stanford, CA, USA
3
Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, Piscataway, NJ, USA
4
CERN, Geneva, Switzerland
5
IRFU-CEA, Université Paris-Saclay, 91191, Gif-sur-Yvette, France
6
Institute of Experimental Physics SAS, Watsonova 47, 04001, Kosice, Slovak Republic
7
MTA-ELTE Lendület CMS Particle and Nuclear Physics Group, Eötvös Loránd University (ELTE), Budapest, Hungary
8
Laboratory of Particle Accelerator Physics, EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerland
9
Princeton University, Princeton, NJ, USA
Received:
7
July
2023
Accepted:
26
October
2023
Published online:
8
January
2024
At the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), absolute luminosity calibrations obtained by the van der Meer (vdM) method are affected by the mutual electromagnetic interaction of the two beams. The colliding bunches experience relative orbit shifts, as well as optical distortions akin to the dynamic-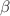 effect, that both depend on the transverse beam separation and must therefore be corrected for when deriving the absolute luminosity scale. In the vdM regime, the beam–beam parameter is small enough that the orbit shift can be calculated analytically. The dynamic-
effect, that both depend on the transverse beam separation and must therefore be corrected for when deriving the absolute luminosity scale. In the vdM regime, the beam–beam parameter is small enough that the orbit shift can be calculated analytically. The dynamic-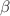 corrections to the luminometer calibrations, however, had until the end of Run 2 been estimated in the linear approximation only. In this report, the influence of beam–beam effects on the vdM-based luminosity scale is quantified, together with the associated systematic uncertainties, by means of simulations that fully take into account the non-linearity of the beam–beam force, as well as the resulting non-Gaussian distortions of the transverse beam distributions. Two independent multiparticle simulations, one limited to the weak-strong approximation and one that models strong-strong effects in a self-consistent manner, are found in excellent agreement; both predict a percent-level shift of the absolute pp-luminosity values with respect to those assumed until recently in the physics publications of the LHC experiments. These results also provide guidance regarding further studies aimed at reducing the beam–beam-related systematic uncertainty on beam–beam corrections to absolute luminosity calibrations by the van der Meer method.
corrections to the luminometer calibrations, however, had until the end of Run 2 been estimated in the linear approximation only. In this report, the influence of beam–beam effects on the vdM-based luminosity scale is quantified, together with the associated systematic uncertainties, by means of simulations that fully take into account the non-linearity of the beam–beam force, as well as the resulting non-Gaussian distortions of the transverse beam distributions. Two independent multiparticle simulations, one limited to the weak-strong approximation and one that models strong-strong effects in a self-consistent manner, are found in excellent agreement; both predict a percent-level shift of the absolute pp-luminosity values with respect to those assumed until recently in the physics publications of the LHC experiments. These results also provide guidance regarding further studies aimed at reducing the beam–beam-related systematic uncertainty on beam–beam corrections to absolute luminosity calibrations by the van der Meer method.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3. SCOAP3 supports the goals of the International Year of Basic Sciences for Sustainable Development.




