https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-023-11742-1
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Spinor domain wall and test fermions on an arbitrary domain wall
1
Department of Theoretical and Nuclear Physics, Al-Farabi Kazakh National University, 050040, Almaty, Kazakhstan
2
Institute of Experimental and Theoretical Physics, Al-Farabi Kazakh National University, 050040, Almaty, Kazakhstan
3
Academician J. Jeenbaev Institute of Physics of the NAS of the Kyrgyz Republic, 265a, Chui Street, 720071, Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan
4
Laboratory for Theoretical Cosmology, International Centre of Gravity and Cosmos, Tomsk State University of Control Systems and Radioelectronics (TUSUR), 634050, Tomsk, Russia
Received:
8
May
2023
Accepted:
20
June
2023
Published online:
29
June
2023
We consider a spinor domain wall embedded in a five-dimensional spacetime with a nondiagonal metric. The corresponding plane symmetric solutions for linear and nonlinear spinor fields with different parameters are obtained. It is shown that in the general case the metric functions and spinor fields do not possess 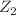 symmetry with respect to the domain wall. We study the angular momentum density of the domain wall arising because of the presence of the spinor field creating the wall. The properties of test fermions located on an arbitrary domain wall are considered. The concepts of the “second spin” (arising due to the properties of the Lorentz group generators in a five-dimensional spacetime) and of the “second magnetic field” (representing the components
symmetry with respect to the domain wall. We study the angular momentum density of the domain wall arising because of the presence of the spinor field creating the wall. The properties of test fermions located on an arbitrary domain wall are considered. The concepts of the “second spin” (arising due to the properties of the Lorentz group generators in a five-dimensional spacetime) and of the “second magnetic field” (representing the components 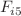 of the electromagnetic field five-tensor) are introduced. We find eigenspinors of the “second spin” and show that some of them represent the Bell states. In the nonrelativistic limit we derive the Pauli equation for the test fermions on the domain wall which contains an extra term describing the interaction of a spin-1/2 particle with the “second magnetic field”; this allows the possibility of an experimental verification of the existence of extra dimensions.
of the electromagnetic field five-tensor) are introduced. We find eigenspinors of the “second spin” and show that some of them represent the Bell states. In the nonrelativistic limit we derive the Pauli equation for the test fermions on the domain wall which contains an extra term describing the interaction of a spin-1/2 particle with the “second magnetic field”; this allows the possibility of an experimental verification of the existence of extra dimensions.
© The Author(s) 2023
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3. SCOAP3 supports the goals of the International Year of Basic Sciences for Sustainable Development.




