https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-025-14496-0
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Chameleon gravity as an alternative to dark matter
1
Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Malayer University, Malayer, Iran
2
Department of Physics, Shahid Beheshti University, 1983969411, Tehran, Iran
a
r.zaregonbadi@malayeru.ac.ir
Received:
8
April
2025
Accepted:
4
July
2025
Published online:
18
July
2025
By studying the chameleon gravity on galaxy scales, we investigate the effects of the chameleon dark matter. To perform this task, we consider the dynamics of the chameleon scalar field in the region of galactic halos in static spherically symmetric spacetimes that differ only slightly from classical general relativity, but have similar symmetry behind this region. Hence, we demonstrate its ability to act as dark matter. In fact, by obtaining the expression for the tangential speed in this region, we apply this approach to explain the issue of flat galactic rotation curves. We obtain that the mass associated with the chameleon scalar field varies linearly with the radius of galaxy, and hence, the tangential speed in that region is constant, which is consistent with observational data without any need to introduce a mysterious dark matter. Accordingly, we show that the presented chameleon gravity has a well-defined Newtonian limit and can describe the geometry of spacetime in the region of flat galactic rotation curves, and is consistent with the corresponding results of the 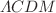 model with the NFW profile. We also consider a test particle moving in a timelike geodesic and obtain the fifth-force, which varies proportionally to the inverse of the radius of galaxy. Moreover, we obtain the effects on the angle representing the deflection of light and on the time representing the radar echo delay of photons passing through the region of galactic halos. We show that as the radius of galaxy increases, the effect on the angle of light passing through the region around galactic halos decreases. Also, the obtained result indicates that the relevant time delay decreases with increasing radius towards the end of the galactic halo.
model with the NFW profile. We also consider a test particle moving in a timelike geodesic and obtain the fifth-force, which varies proportionally to the inverse of the radius of galaxy. Moreover, we obtain the effects on the angle representing the deflection of light and on the time representing the radar echo delay of photons passing through the region of galactic halos. We show that as the radius of galaxy increases, the effect on the angle of light passing through the region around galactic halos decreases. Also, the obtained result indicates that the relevant time delay decreases with increasing radius towards the end of the galactic halo.
© The Author(s) 2025
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




