https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-025-14385-6
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Impact of quantum-corrected parameter on spinning particle motion around a black hole
1
National Research University TIIAME, Kori Niyoziy 39, 100000, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
2
Tashkent State Technical University, 100095, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
3
Urgench State University, Kh. Alimdjan str. 14, 220100, Urgench, Uzbekistan
4
New Uzbekistan University, Movarounnahr street 1, 100000, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
5
School of Physics, Harbin Institute of Technology, 150001, Harbin, People’s Republic of China
6
Department of Physics, Zhejiang Normal University, 321004, Jinhua, People’s Republic of China
7
Research Center of Astrophysics and Cosmology, Khazar University, 41 Mehseti Street, AZ1096, Baku, Azerbaijan
8
School of Science, Walailak University, 80160, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Thailand
9
College of Graduate Studies, Walailak University, 80160, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Thailand
a
phongpichit.ch@mail.wu.ac.th
Received:
8
April
2025
Accepted:
20
May
2025
Published online:
11
June
2025
The motion of spinning particles around a quantum-corrected black hole is examined in this paper. We investigate the dynamics of spinning test particles by using the Mathisson–Papapetrou–Dixon equations, the Tulczyjew spin-supplementary condition, and restricting the motion to the equatorial plane. We determine the innermost stable circular orbit (ISCO), effective potential, and effective force and examine how these depend on the black hole’s 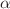 parameter and the particle’s s spin. However, we also take into account a superluminal bound on the motion of the spinning particle since its kinematical four-velocity and dynamical four-momentum are not always parallel. We also show how the parameter
parameter and the particle’s s spin. However, we also take into account a superluminal bound on the motion of the spinning particle since its kinematical four-velocity and dynamical four-momentum are not always parallel. We also show how the parameter 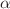 affects the maximum value of the spin parameter s. We determine the critical angular momentum of the particle for which a collision is possible by investigating collisions of spinning particles close to the horizon of a black hole. Finally, we compute the particle’s center-of-mass energy
affects the maximum value of the spin parameter s. We determine the critical angular momentum of the particle for which a collision is possible by investigating collisions of spinning particles close to the horizon of a black hole. Finally, we compute the particle’s center-of-mass energy 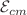 and analyze how the spin of the colliding particles affects it.
and analyze how the spin of the colliding particles affects it.
© The Author(s) 2025
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




