https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-025-14081-5
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Particles dynamics with QPOs and thermodynamics features around a deformed anti-de sitter Schwarzschild black hole
1
School of Mathematical Sciences, Zhejiang Normal University, 321004, Jinhua, Zhejiang, China
2
Department of Mathematics, School of Science, University of Management and Technology, 54000, Lahore, Pakistan
3
Research Center of Astrophysics and Cosmology, Khazar University, 41 Mehseti Street, 1096, Baku, Azerbaijan
4
Laboratory of Theoretical and Applied Physics, Echahid Cheikh Larbi Tebessi University, 12001, Tebessa, Algeria
5
Department of Mathematics, College of Sciences, King Khalid University, 61413, Abha, Saudi Arabia
6
School of Science, Walailak University, 80160, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Thailand
7
College of Graduate Studies, Walailak University, 80160, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Thailand
8
New Uzbekistan University, Movarounnahr Street 1, 100000, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
9
Urgench State University, Kh. Alimdjan str. 14, 220100, Urgench, Uzbekistan
a
phongpichit.ch@mail.wu.ac.th
Received:
27
January
2025
Accepted:
12
March
2025
Published online:
3
April
2025
We explore the dynamics of test particles around a deformed anti-de Sitter Schwarzschild black hole and analyze the influence of model parameters on particle motion. Using the effective potential technique, we examine the stability of equatorial circular orbits. We obtain the analytical expressions for the energy and angular momentum of test particles, along with the innermost stable circular orbits and the effective forces acting upon the test particles. We also probe the epicyclic oscillations of test particles close to the equatorial plane and further evaluate analytical expressions for radial, vertical, and orbital frequencies, including the periastron precession frequency. Additionally, we study the thermal characteristics of the black hole, investigating its Gibbs free energy, emission energy, and check the influence of other thermodynamic properties on the black hole model. Our findings indicate that the model parameters M, 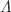 ,
, 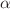 and
and 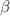 considerably affect both the particle motion including epicyclic oscillations and the thermodynamic behavior.
considerably affect both the particle motion including epicyclic oscillations and the thermodynamic behavior.
© The Author(s) 2025
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




