https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-024-13304-5
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Detection of gamma-ray burst Amati relation based on Hubble data set and Pantheon+ samples
Institute of Theoretical Physics, School of Physics, Dalian University of Technology, 116024, Dalian, People’s Republic of China
Received:
3
June
2024
Accepted:
25
August
2024
Published online:
16
September
2024
Using gamma-ray bursts as standard candles for cosmological parameter constraints rely on their empirical luminosity relations and low-redshift calibration. In this paper, we examine the Amati relation and its potential corrections based on the A118 sample of higher-quality gamma-ray bursts, using both Hubble data set and Pantheon+ samples as calibration samples in the redshift range of 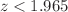 . In calibrating gamma-ray bursts using these two datasets, we employ Gaussian processes to obtain corresponding Hubble diagrams to avoid the dependence on cosmological models in the calibration process. We first divided the low-redshift sample of GRBs into two bins and examined the Amati relation and its potential modifications. We found that under both calibrations, the Amati relation did not show evidence of redshift evolution (68
. In calibrating gamma-ray bursts using these two datasets, we employ Gaussian processes to obtain corresponding Hubble diagrams to avoid the dependence on cosmological models in the calibration process. We first divided the low-redshift sample of GRBs into two bins and examined the Amati relation and its potential modifications. We found that under both calibrations, the Amati relation did not show evidence of redshift evolution (68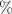 confidence level). For the other two Amati relations that include redshift evolution terms, the central values of the redshift evolution coefficients deviated from 0, but due to the limitations of the sample size and the increase in the number of parameters, most of the redshift evolution coefficients were not able to be excluded from 0 at the 1
confidence level). For the other two Amati relations that include redshift evolution terms, the central values of the redshift evolution coefficients deviated from 0, but due to the limitations of the sample size and the increase in the number of parameters, most of the redshift evolution coefficients were not able to be excluded from 0 at the 1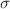 level. Therefore, to assess their situation across the entire redshift range, we employed MCMC to globally fit three types of Amati relations. By computing AIC and BIC, we found that for the GRB A118 sample, the standard Amati relation remains the most fitting empirical luminosity formula, and no potential redshift evolution trend was observed for two different low-redshift calibrating sources.
level. Therefore, to assess their situation across the entire redshift range, we employed MCMC to globally fit three types of Amati relations. By computing AIC and BIC, we found that for the GRB A118 sample, the standard Amati relation remains the most fitting empirical luminosity formula, and no potential redshift evolution trend was observed for two different low-redshift calibrating sources.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.




