https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-024-13039-3
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Charged and magnetized particle motion around a static black hole in the Starobinsky–Bel–Robinson gravity
1
New Uzbekistan University, Mustaqillik avenue 54, 100000, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
2
Ulugh Beg Astronomical Institute, Astronomy St. 33, 100052, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
3
Institute of Fundamental and Applied Research, National Research University TIIAME, Kori Niyoziy 39, 100000, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
4
School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, National University of Sciences and Technology, H-12, Islamabad, Pakistan
5
University of Tashkent for Applied Sciences, Str. Gavhar 1, 100149, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
c
ibrar.hussain@seecs.nust.edu.pk
Received:
16
April
2024
Accepted:
24
June
2024
Published online:
14
July
2024
In this work we focus on the effects of Starobinsky–Bel–Robinson (SBR) gravity parameter and external magnetic field on the motion of charged test particles and magnetic dipoles moving around a black hole in the selected gravity theory. We take the external magnetic field to be uniform and aligned along the axis of symmetry. Our results reveal that the effect of the SBR gravity parameter is very strong in the close environment of the central black hole while in the farther distances this effects diminishes very quickly. We see that the effect of the external magnetic field on the particle motion is always dominating over the SBR gravity parameter in farther distances. We show that for the motion of charged test particles the magnetic interaction can mimic the spin up to very rapid rotations for prograde motion of particles, while for the motion of magnetic dipoles magnetic interaction can mimic the spin completely for retrograde motion of such particles. We observe that in both scenarios, the SBR gravity parameter behaves as a weak mimicker of the spin of Kerr black hole. We apply the outcomes of our study to the scenario where a neutron star is assumed to behave as a magnetic dipole moving around the supermassive black hole Sgr  to investigate how the magnetic field and the SBR gravity coupling parameter
to investigate how the magnetic field and the SBR gravity coupling parameter 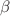 affect the orbits of neutron stars orbiting the supermassive black hole.
affect the orbits of neutron stars orbiting the supermassive black hole.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




