https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-024-13026-8
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Contribution of coherent electron production to measurements of heavy-flavor decayed electrons in heavy-ion collisions
1
Department of Physics, Chongqing Key Laboratory for Strongly Coupled Physics, Chongqing University, 401331, Chongqing, People’s Republic of China
2
Department of Modern Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026, Hefei, People’s Republic of China
3
Physics Department, Brookhaven National Laboratory, 11973, Upton, NY, USA
4
Nuclear Science Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, 94720, Berkeley, CA, USA
5
Institute of Frontier and Interdisciplinary Science, Shandong University, 266237, Qingdao, People’s Republic of China
Received:
28
November
2023
Accepted:
17
June
2024
Published online:
6
July
2024
Heavy quarks, produced at early stages of heavy-ion collisions, are an excellent probe of the Quark-Gluon Plasma (QGP) also created in these collisions. Electrons from open heavy-flavor hadron decays (HFE) are good proxies for heavy quarks, and have been measured extensively in the last two decades to study QGP properties. These measurements are traditionally carried out by subtracting all known background sources from the inclusive electron sample. More recently, a significant enhancement of 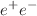 pair production at very low transverse momenta was observed in peripheral heavy-ion collisions. The production characteristics is consistent with coherent photon–photon interactions, which should also constitute a background source to the HFE measurements. In this article, we provide theoretical predictions for the contribution of coherent electron production to HFEs as a function of transverse momentum, centrality and collision energy in Au+Au and Pb+Pb collisions.
pair production at very low transverse momenta was observed in peripheral heavy-ion collisions. The production characteristics is consistent with coherent photon–photon interactions, which should also constitute a background source to the HFE measurements. In this article, we provide theoretical predictions for the contribution of coherent electron production to HFEs as a function of transverse momentum, centrality and collision energy in Au+Au and Pb+Pb collisions.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




