https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-024-12983-4
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Exact cosmological models in metric-affine F(R, T) gravity
1
Centre for Cosmology, Astrophysics and Space Science, GLA University, 281 406, Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, India
2
Department of General and Theoretical Physics, Eurasian International Centre for Theoretical Physics, Eurasian National University, 010008, Astana, Kazakhstan
Received:
1
March
2024
Accepted:
3
June
2024
Published online:
21
June
2024
A flat Friedmann–Lematre–Robertson–Walker (FLRW) spacetime metric was used to investigate some exact cosmological models in metric-affine F(R, T) gravity in this paper. The considered modified Lagrangian function is 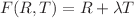 , where R is the Ricci curvature scalar, T is the torsion scalar for the non-special connection, and
, where R is the Ricci curvature scalar, T is the torsion scalar for the non-special connection, and 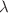 is a model parameter. We also wrote
is a model parameter. We also wrote 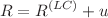 and
and 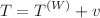 , where
, where 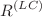 is the Ricci scalar curvature with respect to the Levi–Civita connection and
is the Ricci scalar curvature with respect to the Levi–Civita connection and 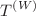 is the torsion scalar with respect to the Weitzenbock connection, and u and v are the functions of scale factor a(t), connection and its derivatives. For the scale factor a(t), we have obtained two exact solutions of modified field equations in two different situations of u and v. Using this scale factor, we have obtained various geometrical parameters to investigate the universe’s cosmological properties. We used Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) simulation to analyze two types of latest datasets: cosmic chronometer (CC) data (Hubble data) points and Pantheon SNe Ia samples, and found the model parameters that fit the observations best at
is the torsion scalar with respect to the Weitzenbock connection, and u and v are the functions of scale factor a(t), connection and its derivatives. For the scale factor a(t), we have obtained two exact solutions of modified field equations in two different situations of u and v. Using this scale factor, we have obtained various geometrical parameters to investigate the universe’s cosmological properties. We used Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) simulation to analyze two types of latest datasets: cosmic chronometer (CC) data (Hubble data) points and Pantheon SNe Ia samples, and found the model parameters that fit the observations best at  , and
, and  regions. We have performed a comparative and relativistic study of geometrical and cosmological parameters. In model-I, we have found that the effective equation of state (EoS) parameter
regions. We have performed a comparative and relativistic study of geometrical and cosmological parameters. In model-I, we have found that the effective equation of state (EoS) parameter 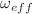 varies in the range
varies in the range 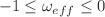 , while in model-II, it varies as
, while in model-II, it varies as 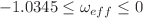 . We found that both models are transit phase (moving from slowing down to speeding up) universes with a transition redshift
. We found that both models are transit phase (moving from slowing down to speeding up) universes with a transition redshift  and
and  .
.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




