https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-024-12768-9
Regular Article - Experimental Physics
Muon-induced background in a next-generation dark matter experiment based on liquid xenon
1
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Sheffield, S3 7RH, Sheffield, UK
2
Department of Physics, Imperial College London, SW7 2AZ, London, UK
3
FZU-Institute of Physics of the Czech Academy of Sciences, 182 00, Prague, Czech Republic
Received:
14
November
2023
Accepted:
8
April
2024
Published online:
9
May
2024
Muon-induced neutrons can lead to potentially irreducible backgrounds in rare event search experiments. We have investigated the implication of laboratory depth on the muon-induced background in a future dark matter experiment capable of reaching the so-called neutrino floor. Our simulation study focused on a xenon-based detector with 70 tonnes of active mass, surrounded by additional veto systems plus a water shield. Two locations at the Boulby Underground Laboratory (UK) were analysed as examples: an experimental cavern in salt at a depth of 2850 m w. e. (similar to the location of the existing laboratory), and a deeper laboratory located in polyhalite rock at a depth of 3575 m w. e. Our results show that no cosmogenic background events are likely to survive standard analysis cuts for 10 years of operation at either location. The largest background component we identified comes from beta-delayed neutron emission from 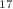 N which is produced from
N which is produced from 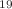 F in the fluoropolymer components of the experiment. Our results confirm that a dark matter search with sensitivity to the neutrino floor is viable (from the point of view of cosmogenic backgrounds) in underground laboratories at these levels of rock overburden. This work was conducted in 2019–21 in the context of a feasibility study to investigate the possibility of developing the Boulby Underground Laboratory to host a next-generation dark matter experiment; however, our findings are also relevant for other underground laboratories.
F in the fluoropolymer components of the experiment. Our results confirm that a dark matter search with sensitivity to the neutrino floor is viable (from the point of view of cosmogenic backgrounds) in underground laboratories at these levels of rock overburden. This work was conducted in 2019–21 in the context of a feasibility study to investigate the possibility of developing the Boulby Underground Laboratory to host a next-generation dark matter experiment; however, our findings are also relevant for other underground laboratories.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




