https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-024-12549-4
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Cosmological constraints on  gravity with redshift space distortion data
gravity with redshift space distortion data
1
Laboratory of Physics of Matter and Radiations, Mohammed I University, BP 717, Oujda, Morocco
2
Higher School of Education and Training, Mohammed I University, BP 717, Oujda, Morocco
Received:
29
November
2023
Accepted:
11
February
2024
Published online:
24
March
2024
In this paper, we explore one of Einstein’s alternative formulations which involves the non-metricity scalar, Q, within the framework of f(Q) theory. Our study focuses on solving the modified Friedmann equations for the case of dust matter,  , and a form of
, and a form of 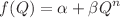 . We investigate the behavior of our model in both linear
. We investigate the behavior of our model in both linear 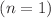 and nonlinear
and nonlinear 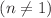 scenarios at the background and perturbation levels. By employing the Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) method, we constrain our model using observational datasets including redshift space distortion, cosmic chronometers, and Pantheon
scenarios at the background and perturbation levels. By employing the Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) method, we constrain our model using observational datasets including redshift space distortion, cosmic chronometers, and Pantheon . Without using any parameterization of the growth rate index which quantifies the deviation from the
. Without using any parameterization of the growth rate index which quantifies the deviation from the 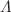 CDM model, both models exhibit good accuracy in describing the redshift space distortion. We further analyze the dynamics of the Universe using cosmography parameters, where our model exhibits a phase transition between deceleration and acceleration phases at
CDM model, both models exhibit good accuracy in describing the redshift space distortion. We further analyze the dynamics of the Universe using cosmography parameters, where our model exhibits a phase transition between deceleration and acceleration phases at 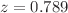 . Our findings reveal that our model exhibits a phantom-like behavior based on statefinder diagnostic analysis. Interestingly, the model demonstrates a rich variety of behaviors, resembling either a quintessence-like scenario for
. Our findings reveal that our model exhibits a phantom-like behavior based on statefinder diagnostic analysis. Interestingly, the model demonstrates a rich variety of behaviors, resembling either a quintessence-like scenario for 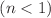 or phantom-like scenario for
or phantom-like scenario for 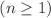 . Using the MCMC best fit and parameterizing the growth index, the evolution of the growth index also depends on the parameter n, either remaining constant (in the linear case) or showing a decreasing trend (in the nonlinear case), indicating a weaker growth rate of density perturbations during earlier cosmic times. Finally, we compare our findings of the growth index with the values obtained in the literature.
. Using the MCMC best fit and parameterizing the growth index, the evolution of the growth index also depends on the parameter n, either remaining constant (in the linear case) or showing a decreasing trend (in the nonlinear case), indicating a weaker growth rate of density perturbations during earlier cosmic times. Finally, we compare our findings of the growth index with the values obtained in the literature.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




