https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-023-12356-3
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Simultaneous measurements on cosmic curvature and opacity using latest HII regions and H(z) observations
1
Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Intelligent Sensors and Advanced Sensor Materials, School of Physics and Electronics, Hunan University of Science and Technology, 411201, Xiangtan, China
2
School of Physics and Optoelectronic, Yangtze University, 434023, Jingzhou, China
3
National Centre for Nuclear Research, Pasteura 7, 02-093, Warsaw, Poland
4
Department of Physics, Liaoning Normal University, 116029, Dalian, China
Received:
23
July
2023
Accepted:
14
December
2023
Published online:
4
January
2024
The different spatial curvatures of the universe affect the measurement of cosmological distances, which may also contribute to explaining the observed dimming of type Ia supernovae. This phenomenon may be caused by the opacity of the universe. Similarly, the opacity of the universe can lead to a bias in our measurements of curvature. Thus, it is necessary to measure cosmic curvature and opacity simultaneously. In this paper, we propose a new model-independent method to simultaneously measure the cosmic curvature and opacity by using the latest observations of HII galaxies acting as standard candles and the latest Hubble parameter observations. The machine learning method-Artificial Neural Network is adopted to reconstruct observed Hubble parameter H(z) observations. Our results support a slightly opaque and flat universe at 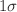 confidence level by using previous 156 HII regions sample. However, the negative curvature is obtained by using the latest 181 HII regions sample in the redshift range
confidence level by using previous 156 HII regions sample. However, the negative curvature is obtained by using the latest 181 HII regions sample in the redshift range 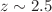 . More importantly, we obtain the simultaneous measurements with precision on the cosmic opacity
. More importantly, we obtain the simultaneous measurements with precision on the cosmic opacity 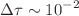 and curvature
and curvature 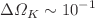 . A strong degeneracy between the cosmic opacity and curvature parameters is also revealed in this analysis.
. A strong degeneracy between the cosmic opacity and curvature parameters is also revealed in this analysis.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3. SCOAP3 supports the goals of the International Year of Basic Sciences for Sustainable Development.




