https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-023-12284-2
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Sequential Monte Carlo with cross-validated neural networks for complexity of hyperbolic black hole solutions in 4D
1
Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St John’s, NL, Canada
2
Research Group GRAM, Department of Signal Theory and Communications, University of Alcalá, Alcalá de Henares, Spain
b ehsan.hatefi@uah.es, ehsanhatefi@gmail.com
Received:
16
August
2023
Accepted:
23
November
2023
Published online:
29
November
2023
This paper investigates the self-similar solutions of the Einstein-axion-dilaton configuration from type IIB string theory and the global SL(2,R) symmetry. We consider the Continuous Self Similarity (CSS), where the scale transformation is controlled by an SL(2, R) boost or hyperbolic translation. The solutions stay invariant under the combination of space-time dilation with internal SL(2,R) transformations. We develop a new formalism based on Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) and artificial neural networks (NNs) to estimate the self-similar solutions to the equations of motion in the hyperbolic class in four dimensions. Due to the complex and highly nonlinear patterns, researchers typically have to use various constraints and numerical approximation methods to estimate the equations of motion; thus, they have to overlook the measurement errors in parameter estimation. Through a Bayesian framework, we incorporate measurement errors into our models to find the solutions to the hyperbolic equations of motion. It is well known that the hyperbolic class suffers from multiple solutions where the critical collapse functions have overlap domains for these solutions. To deal with this complexity, for the first time in literature on the axion-dilaton system, we propose the SMC approach to obtain the multi-modal posterior distributions. Through a probabilistic perspective, we confirm the deterministic 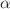 and
and 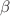 solutions available in the literature and determine all possible solutions that may occur due to measurement errors. We finally proposed the penalized Leave-One-Out Cross-validation (LOOCV) to combine the Bayesian NN-based estimates optimally. The approach enables us to determine the optimum weights while dealing with the co-linearity issue in the NN-based estimates and better predict the critical functions corresponding to multiple solutions of the equations of motion.
solutions available in the literature and determine all possible solutions that may occur due to measurement errors. We finally proposed the penalized Leave-One-Out Cross-validation (LOOCV) to combine the Bayesian NN-based estimates optimally. The approach enables us to determine the optimum weights while dealing with the co-linearity issue in the NN-based estimates and better predict the critical functions corresponding to multiple solutions of the equations of motion.
© The Author(s) 2023
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3. SCOAP3 supports the goals of the International Year of Basic Sciences for Sustainable Development.




