https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-023-12205-3
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Strong gravitational lensing by loop quantum gravity motivated rotating black holes and EHT observations
1
Centre for Theoretical Physics, Jamia Millia Islamia, 110025, New Delhi, India
2
Astrophysics and Cosmology Research Unit, School of Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science, University of KwaZulu-Natal, Private Bag 54001, 4000, Durban, South Africa
Received:
8
August
2023
Accepted:
28
October
2023
Published online:
8
November
2023
We investigate gravitational lensing in the strong deflection regime by loop quantum gravity (LQG)-motivated rotating black hole (LMRBH) metrics with an additional parameter l besides mass M and rotation a. The LMRBH spacetimes are regular everywhere, asymptotically encompassing the Kerr black hole as a particular case and, depending on the parameters, describe black holes with one horizon only (BH-I), black holes with an event horizon and a Cauchy horizon (BH-II), black holes with three horizons (BH-III), or black holes with no horizons (NH) spacetime. It turns out that as the LQG parameter l increases, the unstable photon orbit radius 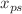 , the critical impact parameter
, the critical impact parameter 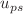 , the deflection angle
, the deflection angle 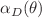 and angular position
and angular position  also increases. Meanwhile, the angular separation s decreases, and relative magnitude
also increases. Meanwhile, the angular separation s decreases, and relative magnitude  increases with increasing l for prograde motion but they show opposite behaviour for the retrograde motion. Using supermassive black holes (SMBH) Sgr A* and M87* as lenses, we compare the observable signatures of LMRBH with those of Kerr black holes. For Sgr A*, the angular position
increases with increasing l for prograde motion but they show opposite behaviour for the retrograde motion. Using supermassive black holes (SMBH) Sgr A* and M87* as lenses, we compare the observable signatures of LMRBH with those of Kerr black holes. For Sgr A*, the angular position 
 (16.4, 39.8)
(16.4, 39.8) 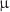 as, while for M87*
as, while for M87*  (12.33, 29.9)
(12.33, 29.9) 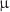 as. The angular separation s, for SMBHs Sgr A* and M87*, differs significantly, with values ranging
as. The angular separation s, for SMBHs Sgr A* and M87*, differs significantly, with values ranging  (0.008–0.376)
(0.008–0.376) 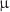 as for Sgr A* and
as for Sgr A* and  (0.006–0.282)
(0.006–0.282) 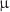 as for M87*. The deviations of the lensing observables
as for M87*. The deviations of the lensing observables 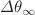 and
and  for LMRBH (
for LMRBH ( ) from Kerr black holes can reach up to
) from Kerr black holes can reach up to  as and
as and  as for Sgr A*, and
as for Sgr A*, and 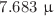 as and
as and 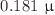 as for M87*. The relative magnitude
as for M87*. The relative magnitude 
 (0.047, 1.54). We estimate the time delay between the first and second relativistic images using twenty supermassive galactic centre black holes as lenses to find, for example, the time delay for Sgr A* and M87* can reach approximately 23.26 min and 33,261.8 min, respectively. Our analysis concludes that, within the
(0.047, 1.54). We estimate the time delay between the first and second relativistic images using twenty supermassive galactic centre black holes as lenses to find, for example, the time delay for Sgr A* and M87* can reach approximately 23.26 min and 33,261.8 min, respectively. Our analysis concludes that, within the 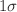 region, a significant portion of the BH-I and BH-II parameter space agrees with the EHT results of M87* and Sgr A*. The possibility of LMRBH being a BH-III with three horizons has been almost ruled out, except for a small portion of parameter space, by
region, a significant portion of the BH-I and BH-II parameter space agrees with the EHT results of M87* and Sgr A*. The possibility of LMRBH being a BH-III with three horizons has been almost ruled out, except for a small portion of parameter space, by  bounds of Sgr A* and M87* measured by EHT. In contrast, NH without a horizon is completely ruled out. We discover that the EHT results of Sgr A* place more stringent limits on the parameter space of LMRBH black holes than those established by the EHT results of M87*.
bounds of Sgr A* and M87* measured by EHT. In contrast, NH without a horizon is completely ruled out. We discover that the EHT results of Sgr A* place more stringent limits on the parameter space of LMRBH black holes than those established by the EHT results of M87*.
© The Author(s) 2023
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.




