https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-023-12141-2
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
A comprehensive study of Bardeen stars with conformal motion in 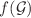 gravity
gravity
1
National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences, Lahore Campus, Lahore, Pakistan
2
School of Mathematical Sciences, Zhejiang Normal University, Jinhua, Zhejiang, China
3
Department of Mathematics, University of Management and Technology, Sialkot Campus, Lahore, Pakistan
4
School of Mathematical Sciences, Queen Mary University of London, London, UK
b adnan.malik@zjnu.edu.cn, adnan.malik@skt.umt.edu.pk, adnanmalik_chheena@yahoo.com
Received:
17
August
2023
Accepted:
13
October
2023
Published online:
4
November
2023
In this manuscript, we use the conformal killing vectors to solve the Einstein–Maxwell field equations in the background of modified 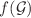 gravity. We consider the observational data for four different stars namely
gravity. We consider the observational data for four different stars namely  ,
, 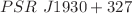 ,
,  and
and 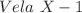 respectively. By using the data, we derive the physical parameters from the matching criteria using conformal killing vectors and the exterior Bardeen geometry. Furthermore, several physical properties of compact stellar structures are examined in order to achieve the physical validity and stability for considered models. The graphical analysis including energy density, pressure components, equation of state parameters, and energy conditions are examined. Moreover, the equilibrium conditions through Tolman–Oppenheimer–Volkoff equation and stability criteria through adiabatic index for the charged stellar structure study are investigated. It is worth noting that all of these compact objects are physically viable and stable under conformal motion in context of Bardeen geometry for two different models of
respectively. By using the data, we derive the physical parameters from the matching criteria using conformal killing vectors and the exterior Bardeen geometry. Furthermore, several physical properties of compact stellar structures are examined in order to achieve the physical validity and stability for considered models. The graphical analysis including energy density, pressure components, equation of state parameters, and energy conditions are examined. Moreover, the equilibrium conditions through Tolman–Oppenheimer–Volkoff equation and stability criteria through adiabatic index for the charged stellar structure study are investigated. It is worth noting that all of these compact objects are physically viable and stable under conformal motion in context of Bardeen geometry for two different models of 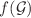 theory of gravity. Conclusively, the results show that f(G) gravity with Bardeen model may provide more massive stellar objects as compared to general relativity.
theory of gravity. Conclusively, the results show that f(G) gravity with Bardeen model may provide more massive stellar objects as compared to general relativity.
© The Author(s) 2023
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.




