https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-024-13334-z
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
New charged anisotropic solution in f(Q)-gravity and effect of non-metricity and electric charge parameters on constraining maximum mass of self-gravitating objects
1
Department of Mathematical and Physical Sciences, College of Arts and Sciences, University of Nizwa, P.O. Box 33, 616, Nizwa, Sultanate of Oman
2
School of Mathematical Sciences, Zhejiang Normal University, 321004, Jinhua, Zhejiang, China
3
Department of Physics, Zhejiang Normal University, 321004, Jinhua, People’s Republic of China
a
sunil@unizwa.edu.om
b
asifamustafa3828@gmail.com
Received:
5
March
2024
Accepted:
4
September
2024
Published online:
27
September
2024
In the present article, A new class of singularity-free charged anisotropic stars is derived in f(Q)-gravity regime. To solve the field equations, we assume a particular form of anisotropy along with an electric field and obtain a new exact solution in f(Q)-gravity. The explicit mathematical expression for the model parameters is derived by the smooth joining of the obtained solutions with the exterior Reissner–Nordstrom de-Sitter solution across the bounding surface of a compact star along with the requirement that the radial pressure vanishes at the boundary. We have modeled four self-gravitating pulsar objects such as LMC X-4, PSR J1903+327, PSR J1614-2230, and GW190814 in our current study and predict the radii of these objects that fall between 8 and 10 km. Furthermore, the physical validity of the solution is performed for self-gravitating object PSR J1614-2230 with mass 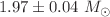 with radius 10 km. The solution successfully fulfills all the physical requirements along with the stability and hydrostatic equilibrium conditions for a well-behaved model. The non-metricity f(Q)-parameter
with radius 10 km. The solution successfully fulfills all the physical requirements along with the stability and hydrostatic equilibrium conditions for a well-behaved model. The non-metricity f(Q)-parameter 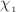 and electric charge parameter
and electric charge parameter 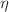 play an important role in the maximum mass of the objects. The maximum mass increases when
play an important role in the maximum mass of the objects. The maximum mass increases when 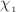 and
and 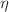 increase but a non-collapsing stable object can be obtained when
increase but a non-collapsing stable object can be obtained when 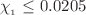 and
and 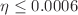 .
.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.




