https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-022-10330-z
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Anisotropy of the gravitational-wave standard sirens and its cosmological applications
Institute of Theoretical Physics, School of Physics, Dalian University of Technology, 116024, Dalian, China
Received:
18
January
2022
Accepted:
13
April
2022
Published online:
29
April
2022
We analyze the anisotropic factors present in the gravitational wave signal, such as the peculiar velocity of the observer and the inhomogeneous distribution of matter in the universe. We model the gravitational wave source as a standard siren, extract the anisotropic part of its luminosity distance 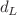 , and obtain the Hubble parameter H(z) by direct calculation instead of integration. Finally, we derive the equation of state
, and obtain the Hubble parameter H(z) by direct calculation instead of integration. Finally, we derive the equation of state 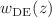 for the dark energy by both model-dependent and model-independent methods, and further investigate the cosmological significance of the simulated H(z) measurements. The advantage of this approach is that it makes full use of the anisotropic part of the
for the dark energy by both model-dependent and model-independent methods, and further investigate the cosmological significance of the simulated H(z) measurements. The advantage of this approach is that it makes full use of the anisotropic part of the 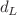 data, which directly gives the value of H(z) at certain redshifts. This approach is sensitive to the local features of H(z) and does not depend on the cosmological model.
data, which directly gives the value of H(z) at certain redshifts. This approach is sensitive to the local features of H(z) and does not depend on the cosmological model.
© The Author(s) 2022
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3




