https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-021-09506-w
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
The origin of rest-mass energy
Department of Physics, The Applied Math Program, and Department of Astronomy, The University of Arizona, 85721, Tucson, AZ, USA
Received:
27
June
2021
Accepted:
28
July
2021
Published online:
7
August
2021
Today we have a solid, if incomplete, physical picture of how inertia is created in the standard model. We know that most of the visible baryonic ‘mass’ in the Universe is due to gluonic back-reaction on accelerated quarks, the latter of which attribute their own inertia to a coupling with the Higgs field – a process that elegantly and self-consistently also assigns inertia to several other particles. But we have never had a physically viable explanation for the origin of rest-mass energy, in spite of many attempts at understanding it towards the end of the nineteenth century, culminating with Einstein’s own landmark contribution in his Annus Mirabilis. Here, we introduce to this discussion some of the insights we have garnered from the latest cosmological observations and theoretical modeling to calculate our gravitational binding energy with that portion of the Universe to which we are causally connected, and demonstrate that this energy is indeed equal to 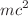 when the inertia m is viewed as a surrogate for gravitational mass.
when the inertia m is viewed as a surrogate for gravitational mass.
John Woodruff Simpson Fellow.
© The Author(s) 2021
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3




