https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-019-7379-y
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Principal component analysis of collective flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions
1
Department of Physics and State Key Laboratory of Nuclear Physics and Technology, Peking University, Beijing, 100871, China
2
Collaborative Innovation Center of Quantum Matter, Beijing, 100871, China
3
Center for High Energy Physics, Peking University, Beijing, 100871, China
* e-mail: Huichaosong@pku.edu.cn
Received:
24
August
2019
Accepted:
6
October
2019
Published online:
23
October
2019
In this paper, we implement principal component analysis (PCA) to study the single particle distributions generated from thousands of  hydrodynamic simulations with an aim to explore if a machine could directly discover flow from the huge amount of data without explicit instructions from human-beings. We found that the obtained PCA eigenvectors are similar to but not identical with the traditional Fourier bases. Correspondingly, the PCA defined flow harmonics
hydrodynamic simulations with an aim to explore if a machine could directly discover flow from the huge amount of data without explicit instructions from human-beings. We found that the obtained PCA eigenvectors are similar to but not identical with the traditional Fourier bases. Correspondingly, the PCA defined flow harmonics  are also similar to the traditional
are also similar to the traditional  for
for 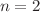 and 3, but largely deviated from the Fourier ones for
and 3, but largely deviated from the Fourier ones for 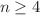 . A further study on the symmetric cumulants and the Pearson coefficients indicates that mode-coupling effects are reduced for these flow harmonics defined by PCA.
. A further study on the symmetric cumulants and the Pearson coefficients indicates that mode-coupling effects are reduced for these flow harmonics defined by PCA.
© The Author(s), 2019




