https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-025-14446-w
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Echoes and quasi-normal modes of perturbations around Schwarzschild traversable wormholes
1
School of Fundamental Physics and Mathematical Sciences, Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, UCAS, 310024, Hangzhou, China
2
School of Physics, Nankai University, Weijin Road 94, 300071, Tianjin, China
3
Faculty of Physics, University of Vienna, Boltzmanngasse 5, 1090, Vienna, Austria
Received:
16
March
2025
Accepted:
18
June
2025
Published online:
5
July
2025
We investigate the waveforms and quasi-normal modes around Schwarzschild traversable wormholes under different field perturbations, including the scalar field, the electromagnetic (vector) field, and the axial gravitational (tensor) field perturbations. Our results indicate that under the influence of the matter at the throat of the wormhole, a Dirac 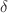 -function distribution of matter appears in the effective potentials of the scalar and axial gravitational perturbations and it affects the propagation of these two types of perturbations in spacetime. However, the matter at the throat has no influence on the propagation of electromagnetic perturbations. Furthermore, we quantify the impact of throat matter on both the perturbation waveforms and quasi-normal modes for all three field types. Through comparative studies between Schwarzschild traversable wormholes and Schwarzschild black holes, we identify two distinct features. Firstly, the perturbation waveforms exhibit echoes and damping oscillations around wormholes, whereas they solely display damping oscillations around black holes. Secondly, the difference between the adjacent peaks varies with the mass parameter and the throat radial coordinate in the waveform around Schwarzschild traversable wormholes, while a constant peak spacing occurs, which is determined solely by mass, in the waveform around Schwarzschild black holes. Based on these findings, we propose a framework to estimate the mass parameter and throat radial coordinate of Schwarzschild traversable wormholes through waveforms and quasi-normal modes. Our analyses provide a more profound comprehension of the inherent characteristics of Schwarzschild traversable wormholes.
-function distribution of matter appears in the effective potentials of the scalar and axial gravitational perturbations and it affects the propagation of these two types of perturbations in spacetime. However, the matter at the throat has no influence on the propagation of electromagnetic perturbations. Furthermore, we quantify the impact of throat matter on both the perturbation waveforms and quasi-normal modes for all three field types. Through comparative studies between Schwarzschild traversable wormholes and Schwarzschild black holes, we identify two distinct features. Firstly, the perturbation waveforms exhibit echoes and damping oscillations around wormholes, whereas they solely display damping oscillations around black holes. Secondly, the difference between the adjacent peaks varies with the mass parameter and the throat radial coordinate in the waveform around Schwarzschild traversable wormholes, while a constant peak spacing occurs, which is determined solely by mass, in the waveform around Schwarzschild black holes. Based on these findings, we propose a framework to estimate the mass parameter and throat radial coordinate of Schwarzschild traversable wormholes through waveforms and quasi-normal modes. Our analyses provide a more profound comprehension of the inherent characteristics of Schwarzschild traversable wormholes.
© The Author(s) 2025
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




