https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-025-14425-1
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Chaotic motion of charged test particles in a Kerr-MOG black hole with explicit symplectic algorithms
1
School of Mathematics and Statistics, Hubei Minzu University, 445000, Enshi, China
2
College of Intelligent Systems Science and Engineering, Hubei Minzu University, 445000, Enshi, China
3
School of Physics and Technology, University of Jinan, 250022, Jinan, China
Received:
29
December
2024
Accepted:
10
June
2025
Published online:
15
July
2025
The Kerr-MOG black hole has recently attracted significant research attention and has been extensively applied in various fields. To accurately characterize the long-term dynamical evolution of charged particles around a Kerr-MOG black hole, it is essential to utilize numerical algorithms that are high-precision, stable, and capable of preserving the inherent physical structural properties. In this study, we employ explicit symplectic algorithms combined with the Hamiltonian splitting technique to numerically solve the equations of motion for charged particles. Initially, by decomposing the Hamiltonian into five integrable components, three distinct explicit symplectic algorithms (S2, S4, and 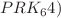 are constructed. Numerical experiments reveal that the
are constructed. Numerical experiments reveal that the 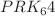 algorithm achieves superior accuracy. Subsequently, we utilize Poincaré sections and the fast Lyapunov indicator (FLI) to investigate the dynamic evolution of the particle. Our numerical results demonstrate that the energy E, angular momentum L, magnetic field parameter
algorithm achieves superior accuracy. Subsequently, we utilize Poincaré sections and the fast Lyapunov indicator (FLI) to investigate the dynamic evolution of the particle. Our numerical results demonstrate that the energy E, angular momentum L, magnetic field parameter 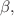 black hole spin parameter a, and MOG parameter
black hole spin parameter a, and MOG parameter 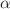 all significantly influence the particle’s motion. Specifically, the chaotic region expands with an increase in E,
all significantly influence the particle’s motion. Specifically, the chaotic region expands with an increase in E, 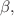 or
or 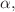 but contracts with an increase in a or L. Furthermore, when any two of these five parameters are varied simultaneously, it becomes evident that a and L predominantly dictate the system’s behavior. This study not only offers novel insights into the chaotic dynamics associated with Kerr-MOG black holes but also extends the application of symplectic algorithms in strong gravitational fields.
but contracts with an increase in a or L. Furthermore, when any two of these five parameters are varied simultaneously, it becomes evident that a and L predominantly dictate the system’s behavior. This study not only offers novel insights into the chaotic dynamics associated with Kerr-MOG black holes but also extends the application of symplectic algorithms in strong gravitational fields.
© The Author(s) 2025
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




