https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-025-14373-w
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Analyzing deflection angles and photon sphere dynamics of magnetically charged black holes in nonlinear electrodynamic
1
Department of Physics, Quaid-I-Azam University, 45320, Islamabad, Pakistan
2
Dipartimento di Fisica, Universit‘a degli Studi di Roma “La Sapienza”, Piazzale Aldo Moro 5, 00185, Rome, Italy
3
Electronics Engineering Department, University of Santo Tomas, España Blvd, Sampaloc, 1008, Manila, Metro Manila, Philippines
4
Physics Department, Eastern Mediterranean University, Famagusta, 99628, North Cyprus via Mersin 10, Turkey
5
Physics Department, School of Foundational Studies and Education, Mapúa University, 658 Muralla St., Intramuros, 1002, Manila, Philippines
Received:
23
February
2025
Accepted:
28
May
2025
Published online:
8
June
2025
In this paper, we investigate the gravitational lensing properties of magnetically charged black holes within the framework of nonlinear electrodynamics. We derive the deflection angle and examine the influence of the nonlinear electrodynamics parameter 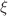 on light bending. We initially employ a geometric approach based on the Gauss–Bonnet theorem to analyze the gravitational deflection of null and timelike particles. This method encapsulates the global characteristics of the lensing effect in an elegant manner. In the subsequent part of the work, we explore the impact of nonlinear electromagnetic corrections on the black hole shadow. Using numerical techniques, we study the behavior of the photon sphere and demonstrate that a reduction in the photon sphere radius leads to a correspondingly smaller shadow. We compare these results with those for the Schwarzschild and Reissner–Nordström black holes, highlighting the distinctive features introduced by nonlinear electrodynamics. Furthermore, we examine the strong deflection limit for light trajectories near these black holes, focusing on the roles of both the magnetic charge
on light bending. We initially employ a geometric approach based on the Gauss–Bonnet theorem to analyze the gravitational deflection of null and timelike particles. This method encapsulates the global characteristics of the lensing effect in an elegant manner. In the subsequent part of the work, we explore the impact of nonlinear electromagnetic corrections on the black hole shadow. Using numerical techniques, we study the behavior of the photon sphere and demonstrate that a reduction in the photon sphere radius leads to a correspondingly smaller shadow. We compare these results with those for the Schwarzschild and Reissner–Nordström black holes, highlighting the distinctive features introduced by nonlinear electrodynamics. Furthermore, we examine the strong deflection limit for light trajectories near these black holes, focusing on the roles of both the magnetic charge 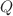 and the nonlinear parameter
and the nonlinear parameter 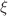 . Our analysis reveals that the combined effects of
. Our analysis reveals that the combined effects of 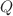 and
and 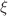 enhance the strong deflection angle, resulting in a more pronounced lensing effect than that predicted by the classical Reissner–Nordström solution. These findings suggest that the nonlinear interactions may provide a potential observational signature for identifying NED black holes.
enhance the strong deflection angle, resulting in a more pronounced lensing effect than that predicted by the classical Reissner–Nordström solution. These findings suggest that the nonlinear interactions may provide a potential observational signature for identifying NED black holes.
© The Author(s) 2025
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




