https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-025-14133-w
Regular Article - Experimental Physics
Search for hadronic decays of feebly-interacting particles at NA62
1
CERN, 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland
2
TRIUMF, Vancouver, BC, Canada
3
University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada
4
Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic
5
CNRS/IN2P3, CPPM, Aix Marseille University, Marseille, France
6
Max-Planck-Institut für Physik (Werner-Heisenberg-Institut), Garching, Germany
7
Institut für Physik and PRISMA Cluster of Excellence, Universität Mainz, Mainz, Germany
8
Dipartimento di Fisica e Scienze della Terra dell’Università e INFN, Sezione di Ferrara, Ferrara, Italy
9
INFN, Sezione di Ferrara, Ferrara, Italy
10
Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia dell’Università e INFN, Sezione di Firenze, Sesto Fiorentino, Italy
11
INFN, Sezione di Firenze, Sesto Fiorentino, Italy
12
Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati, Frascati, Italy
13
Dipartimento di Fisica “Ettore Pancini” e INFN, Sezione di Napoli, Naples, Italy
14
Dipartimento di Fisica e Geologia dell’Università e INFN, Sezione di Perugia, Perugia, Italy
15
INFN, Sezione di Perugia, Perugia, Italy
16
Dipartimento di Fisica dell’Università e INFN, Sezione di Pisa, Pisa, Italy
17
INFN, Sezione di Pisa, Pisa, Italy
18
Scuola Normale Superiore e INFN, Sezione di Pisa, Pisa, Italy
19
Dipartimento di Fisica, Sapienza Università di Roma e INFN, Sezione di Roma I, Rome, Italy
20
INFN, Sezione di Roma I, Rome, Italy
21
INFN, Sezione di Roma Tor Vergata, Rome, Italy
22
Dipartimento di Fisica dell’Università e INFN, Sezione di Torino, Turin, Italy
23
INFN, Sezione di Torino, Turin, Italy
24
Institute of Nuclear Physics, Almaty, Kazakhstan
25
Instituto de Física, Universidad Autónoma de San Luis Potosí, San Luis Potosí, Mexico
26
Horia Hulubei National Institute for R&D in Physics and Nuclear Engineering, Bucharest-Magurele, Romania
27
Faculty of Mathematics, Physics and Informatics, Comenius University, Bratislava, Slovakia
28
CERN, European Organization for Nuclear Research, Geneva, Switzerland
29
Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland
30
School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK
31
School of Physics, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK
32
School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK
33
Physics Department, University of Lancaster, Lancaster, UK
34
Physics and Astronomy Department, George Mason University, Fairfax, VA, USA
35
Authors Affiliated with an International Laboratory Covered by a Cooperation Agreement with CERN, Geneva, Switzerland
36
Authors Affiliated with an Institute Formerly Covered by a Cooperation Agreement with CERN, Geneva, Switzerland
37
Max-Planck-Institut für Physik (Werner-Heisenberg-Institut), 85748, Garching, Germany
38
TRIUMF, V6T 2A3, Vancouver, BC, Canada
39
School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Birmingham, B15 2TT, Birmingham, UK
40
CNRS, IM2NP, Université de Toulon, Aix Marseille University, 83957, La Garde, France
41
Department of Physics, Technical University of Munich, 80333, Munich, Germany
42
Institut für Kernphysik and Helmholtz Institute Mainz, Universität Mainz, 55099, Mainz, Germany
43
CERN, European Organization for Nuclear Research, 1211, Geneva 23, Switzerland
44
Dipartimento di Scienze Fisiche, Informatiche e Matematiche, Università di Modena e Reggio Emilia, 41125, Modena, Italy
45
Faculty of Physics, University of Sofia, 1164, Sofia, Bulgaria
46
Scuola Superiore Meridionale e INFN, Sezione di Napoli, 80138, Naples, Italy
47
Department of Industrial Engineering, University of Roma Tor Vergata, 00173, Rome, Italy
48
Department of Electronic Engineering, University of Roma Tor Vergata, 00173, Rome, Italy
49
Università degli Studi del Piemonte Orientale, 13100, Vercelli, Italy
50
Université Catholique de Louvain, 1348, Louvain-La-Neuve, Belgium
51
Gran Sasso Science Institute, 67100, L’Aquila, Italy
52
al-Farabi Kazakh National University, 050040, Almaty, Kazakhstan
53
Universidad de Guanajuato, 36000, Guanajuato, Mexico
54
INFN, Sezione di Perugia, 06100, Perugia, Italy
55
Charles University, 116 36, Prague 1, Czech Republic
56
Physics Department, University of Lancaster, LA1 4YB, Lancaster, UK
57
Syracuse University, 13244, Syracuse, NY, USA
58
Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati, 00044, Frascati, Italy
59
Dipartimento di Fisica dell’Università e INFN, Sezione di Genova, 16146, Genoa, Italy
60
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Stanford University, 94025, Menlo Park, CA, USA
61
L. N. Gumilyov Eurasian National University, 010000, Nur-Sultan, Kazakhstan
62
Institute of Nuclear Research and Nuclear Energy of Bulgarian Academy of Science (INRNE-BAS), 1784, Sofia, Bulgaria
63
INFN, Sezione di Pisa, 56100, Pisa, Italy
64
CERN, 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland
Received:
7
February
2025
Accepted:
28
March
2025
Published online:
25
May
2025
The NA62 experiment at CERN has the capability to collect data in a beam-dump mode, where 400 GeV protons are dumped on an absorber. In this configuration, New Physics particles, including dark photons, dark scalars, and axion-like particles, may be produced in the absorber and decay in the instrumented volume beginning approximately 80 m downstream of the dump. A search for these particles decaying in flight to hadronic final states is reported, based on an analysis of a sample of 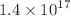 protons on dump collected in 2021. No evidence of a New Physics signal is observed, excluding new regions of parameter spaces of multiple models.
protons on dump collected in 2021. No evidence of a New Physics signal is observed, excluding new regions of parameter spaces of multiple models.
© The Author(s) 2025
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




