https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-025-14079-z
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Forecasts for decaying dark matter from cross-correlation between line intensity mapping and large scale structures surveys
1
School of Physics and Astronomy, Beijing Normal University, 100875, Beijing, China
2
Institute for Frontiers in Astronomy and Astrophysics, Beijing Normal University, 100875, Beijing, China
Received:
24
December
2024
Accepted:
12
March
2025
Published online:
5
April
2025
Axion-like particles (ALPs) are compelling candidates for dark matter with a broad range of possible masses and coupling strengths. These particles decay into two photons, contributing to cosmic background radiation, which may correlate with large-scale structure (LSS). ALPs with a mass around 1 eV decay into monochromatic photons in the near-infrared spectrum, which can be detected by the upcoming SPHEREx mission using line intensity mapping (LIM) technology. To search for ALP signals in SPHEREx, we calculate the cross angular power spectrum between the intensity maps and LSS probes. We employ several LSS probes, including galaxy clustering and weak lensing surveys conducted by the China Space Station Telescope (CSST), as well as CMB lensing performed by CMB-S4. Using a Fisher analysis, we place constraints on the ALP parameters, with uncertainties of 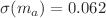 and
and 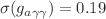 from the joint surveys. Our results suggest that the current bounds on
from the joint surveys. Our results suggest that the current bounds on 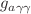 could be improved by an order of magnitude for ALPs in the mass range around 1 eV. The cross-correlation also allows for detection of star formation lines observed by SPHEREx, providing constraints on the amplitude and redshift exponent of their power spectrum with uncertainties of
could be improved by an order of magnitude for ALPs in the mass range around 1 eV. The cross-correlation also allows for detection of star formation lines observed by SPHEREx, providing constraints on the amplitude and redshift exponent of their power spectrum with uncertainties of 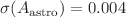 and
and 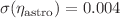 , respectively. Additionally, we consider intrinsic alignment (IA) as a systematic effect in the weak lensing survey. The IA amplitude and exponent are well constrained by the LIM-WL cross-correlation, yielding results of
, respectively. Additionally, we consider intrinsic alignment (IA) as a systematic effect in the weak lensing survey. The IA amplitude and exponent are well constrained by the LIM-WL cross-correlation, yielding results of 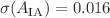 and
and 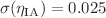 , which offer significant improvements over previous works related to CSST.
, which offer significant improvements over previous works related to CSST.
© The Author(s) 2025
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




