https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-025-14038-8
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Traversable wormholes in constant curvature black holes
1
Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, 208016, Kanpur, India
2
Institut für Theoretische Physik, Leibniz Universität Hannover, Appelstraße 2, 30167, Hannover, Germany
3
Khon Kaen Particle Physics and Cosmology Theory Group (KKPaCT), Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Khon Kaen University, 123 Mitraphap Rd., 40002, Khon Kaen, Thailand
Received:
24
October
2024
Accepted:
3
March
2025
Published online:
28
March
2025
This paper investigates the massive gauge field within spacetime context from a 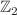 quotient of the constant curvature black hole. We investigate how the matter field’s back reaction affects the spacetime geometry, considering perturbations in the metric up to the first order. The stress-energy tensor’s expectation value can be precisely calculated by evaluating its pull-back onto the covering space. By appropriately selecting boundary conditions for the massive vector field along a non-contractible cycle of the quotient manifold, achieving a negative average energy along a null geodesic becomes feasible, enabling a traversable wormhole.
quotient of the constant curvature black hole. We investigate how the matter field’s back reaction affects the spacetime geometry, considering perturbations in the metric up to the first order. The stress-energy tensor’s expectation value can be precisely calculated by evaluating its pull-back onto the covering space. By appropriately selecting boundary conditions for the massive vector field along a non-contractible cycle of the quotient manifold, achieving a negative average energy along a null geodesic becomes feasible, enabling a traversable wormhole.
© The Author(s) 2025
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




