https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-025-13796-9
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Fermionic entanglement in the presence of background electric and magnetic fields
Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, Haus Khas, 110 016, New Delhi, India
Received:
8
September
2024
Accepted:
10
January
2025
Published online:
25
January
2025
In this study, we investigate the fermionic Schwinger effect in the presence of a constant magnetic field within 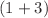 -dimensional Minkowski spacetime, considering both constant and pulsed electric fields. We analyze the correlations between Schwinger pairs for the vacuum and maximally entangled states of two fermionic fields. The correlations are quantified using entanglement entropy and Bell’s inequality violation for the vacuum state, while Bell’s inequality violation and mutual information are used for the maximally entangled state. One can observe the variation of the entanglement produced for fermionic modes with respect to different parameters. Additionally, we discuss the key differences from the behaviour of scalar fields in this context. This study offers deeper insights into quantum field theory and the dynamics of entanglement in the fermionic Schwinger effect.
-dimensional Minkowski spacetime, considering both constant and pulsed electric fields. We analyze the correlations between Schwinger pairs for the vacuum and maximally entangled states of two fermionic fields. The correlations are quantified using entanglement entropy and Bell’s inequality violation for the vacuum state, while Bell’s inequality violation and mutual information are used for the maximally entangled state. One can observe the variation of the entanglement produced for fermionic modes with respect to different parameters. Additionally, we discuss the key differences from the behaviour of scalar fields in this context. This study offers deeper insights into quantum field theory and the dynamics of entanglement in the fermionic Schwinger effect.
© The Author(s) 2025
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




