https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-024-13546-3
Regular Article
Charged Dyson shells supported in curved spacetimes of spherically symmetric central compact objects
1
The Ruppin Academic Center, 40250, Emeq Hefer, Israel
2
The Hadassah Academic College, 91010, Jerusalem, Israel
Received:
18
September
2024
Accepted:
28
October
2024
Published online:
15
November
2024
It is proved that charged thin shells (charged Dyson shells) can be supported in unstable static equilibrium states around spherically symmetric central compact objects. The regime of existence of the composed central-compact-object-static-charged-shell configurations is characterized by the inequalities  , where
, where 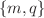 are respectively the proper mass and the electric charge of the supported shell and M is the mass of the central compact object (a black hole or an horizonless compact star). We reveal the physically interesting fact that the supported charged shells become marginally-stable in the
are respectively the proper mass and the electric charge of the supported shell and M is the mass of the central compact object (a black hole or an horizonless compact star). We reveal the physically interesting fact that the supported charged shells become marginally-stable in the 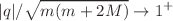 limit, in which case the lifetime (instability timescale) of the composed system can be made arbitrarily large. Our analysis goes beyond the test shell approximation by properly taking into account the exact gravitational and electromagnetic self-interaction energies of the spherically symmetric shell in the curved spacetime. In particular, the existence of the composed compact-object-charged-shell static configurations in the Einstein–Maxwell theory is attributed to the non-linear electromagnetic self-energy of the supported shell.
limit, in which case the lifetime (instability timescale) of the composed system can be made arbitrarily large. Our analysis goes beyond the test shell approximation by properly taking into account the exact gravitational and electromagnetic self-interaction energies of the spherically symmetric shell in the curved spacetime. In particular, the existence of the composed compact-object-charged-shell static configurations in the Einstein–Maxwell theory is attributed to the non-linear electromagnetic self-energy of the supported shell.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.





