https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-024-13077-x
Regular Article - Experimental Physics
Measurement of the background in the CMS muon detector in 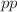 -collisions at
-collisions at 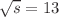

1
Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussel, Belgium
2
Université Libre de Bruxelles, Bruxelles, Belgium
3
Universiteit Gent, Gent, Belgium
4
Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Fisicas, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
5
Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
6
Institute for Nuclear Research and Nuclear Energy, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Sofia, Bulgaria
7
University of Sofia, Sofia, Bulgaria
8
Instituto De Alta Investigación, Universidad de Tarapacá, Arica, Chile
9
Institute of High Energy Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
10
State Key Laboratory of Nuclear Physics and Technology, Peking University, Beijing, China
11
Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China
12
Universidad de Los Andes, Bogota, Colombia
13
Universidad de Antioquia, Medellin, Colombia
14
Academy of Scientific Research and Technology of the Arab Republic of Egypt, Egyptian Network of High Energy Physics, Cairo, Egypt
15
Center for High Energy Physics (CHEP-FU), Fayoum University, El-Fayoum, Egypt
16
Institut de Physique des 2 Infinis de Lyon, Villeurbanne, France
17
Georgian Technical University, Tbilisi, Georgia
18
RWTH Aachen University, III. Physikalisches Institut A, Aachen, Germany
19
Karlsruher Institut für Technologie, Karlsruhe, Germany
20
Institute of Nuclear Research ATOMKI, Debrecen, Hungary
21
Institute of Physics, University of Debrecen, Debrecen, Hungary
22
Panjab University, Chandigarh, India
23
University of Delhi, Delhi, India
24
Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics, Kolkata, India
25
Institute for Research in Fundamental Sciences, Teheran, Iran
26
INFN Sezione di Bari, Università di Bari, Politecnico di Bari, Bari, Italy
27
INFN Sezione di Bologna, Università di Bologna, Bologna, Italy
28
INFN Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati, Frascati, Italy
29
INFN Sezione di Napoli, Università di Napoli ‘Federico II’, Napoli, Italy; Università della Basilicata, Potenza, Italy; Università G. Marconi, Rome, Italy
30
INFN Sezione di Padova, Università di Padova, Padova, Italy; Università di Trento, Trento, Italy
31
INFN Sezione di Pavia, Università di Pavia, Pavia, Italy
32
INFN Sezione di Torino, Università di Torino, Torino, Italy; Università del Piemonte Orientale, Novara, Italy
33
Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea
34
Korea University, Seoul, Korea
35
Kyung Hee University, Department of Physics, Seoul, Korea
36
Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
37
University of Seoul, Seoul, Korea
38
Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, Korea
39
College of Engineering and Technology, American University of the Middle East (AUM), Dasman, Kuwait
40
Centro de Investigacion y de Estudios Avanzados del IPN, Mexico City, Mexico
41
Universidad Iberoamericana, Mexico City, Mexico
42
Benemerita Universidad Autonoma de Puebla, Puebla, Mexico
43
National Centre for Physics, Quaid-I-Azam University, Islamabad, Pakistan
44
Centro de Investigaciones Energéticas Medioambientales y Tecnológicas (CIEMAT), Madrid, Spain
45
Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Madrid, Spain
46
Universidad de Oviedo, Instituto Universitario de Ciencias y Tecnologías Espaciales de Asturias (ICTEA), Oviedo, Spain
47
University of Colombo, Colombo, Sri Lanka
48
University of Ruhuna, Department of Physics, Matara, Sri Lanka
49
CERN, European Organization for Nuclear Research, Geneva, Switzerland
50
Boston University, Boston, MA, USA
51
University of California, Davis, Davis, CA, USA
52
University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA
53
University of California, Riverside, Riverside, CA, USA
54
University of California, Santa Barbara-Department of Physics, Santa Barbara, CA, USA
55
University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA
56
Florida Institute of Technology, Melbourne, FL, USA
57
Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA
58
Northeastern University, Boston, MA, USA
59
Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, USA
60
The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA
61
Rice University, Houston, TX, USA
62
Texas A &M University, College Station, TX, USA
63
Wayne State University, Detroit, MI, USA
64
University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, USA
65
Authors affiliated with an institute or an international laboratory covered by a cooperation agreement with CERN, Geneva, Switzerland
66
Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium
67
Now at Universidad de Antioquia, Medellin, Colombia
68
Now at University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, Wisconsin, USA
69
Cairo University, Gizah, Egypt
70
Helwan University, Cairo, Egypt
71
Now at Zewail City of Science and Technology, Zewail, Egypt
72
Suez University, Suez, Egypt
73
Now at British University in Egypt, Cairo, Egypt
74
Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt
75
Sultan Qaboos University, Muscat, Oman
76
an institute or an international laboratory covered by a cooperation agreement with CERN, Geneva, Switzerland
77
The University of the State of Amazonas, Manaus, Brazil
78
Now at Institute for Research in Fundamental Sciences, Teheran, Iran
79
Faculty of Informatics, University of Debrecen, Debrecen, Hungary
80
Now at CERN, European Organization for Nuclear Research, Geneva, Switzerland
81
Italian National Agency for New Technologies, Energy and Sustainable Economic Development, Bologna, Italy
82
Eastern Mennonite University, Harrisonburg, VA, USA
83
Università degli Studi Guglielmo Marconi, Rome, Italy
84
Scuola Superiore Meridionale, Università di Napoli ‘Federico II’, Naples, Italy
85
CERN, European Organization for Nuclear Research, Geneva, Switzerland
86
Laboratori Nazionali di Legnaro dell’INFN, Legnaro, Italy
87
Now at INFN Sezione di Pisa e Università di Pisa, Pisa, Italy
88
Now at Gran Sasso Science Institute, L’Aquila, Italy
89
Now at Imperial College, London, UK
90
Trincomalee Campus, Eastern University, Nilaveli, Sri Lanka
91
Now at Max Planck Institute for Physics (Werner Heisenberg Institute), Munich, Germany
92
Now at Argonne National Laboratory, Lemont, IL, USA
93
Now at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Karlsruhe, Germany
94
Now at Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA
95
Now at Activision, Santa Monica, CA, USA
96
Now at HRL Laboratories, Malibu, CA, USA
97
Now at Tsung-Dao Lee Institute, Shanghai, China
98
Texas A &M University at Qatar, Doha, Qatar
99
Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea
100
Northeastern University, Boston, MA, USA
101
CERN, 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland
Received:
19
April
2024
Accepted:
1
July
2024
Published online:
27
September
2024
The CMS detector, including its muon system, has been operating at the CERN LHC in increasingly challenging conditions for about 15 years. The muon detector was designed to provide excellent triggering and track reconstruction for muons produced in proton–proton collisons at an instantaneous luminosity (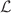 ) of
) of 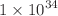 cm
cm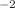 s
s . During the Run 2 data-taking period (2015–2018), the LHC achieved an instantaneous luminosity of twice its design value, resulting in larger background rates and making the efficient detection of muons more difficult. While some backgrounds result from natural radioactivity, cosmic rays, and interactions of the circulating protons with residual gas in the beam pipe, the dominant source of background hits in the muon system arises from proton–proton interactions themselves. Charged hadrons leaving the calorimeters produce energy deposits in the muon chambers. In addition, high-energy particles interacting in the hadron calorimeter and forward shielding elements generate thermal neutrons, which leak out of the calorimeter and shielding structures, filling the CMS cavern. We describe the method used to measure the background rates in the various muon subsystems. These rates, in conjunction with simulations, can be used to estimate the expected backgrounds in the High-Luminosity LHC. This machine will run for at least 10 years starting in 2029 reaching an instantaneous luminosity of
. During the Run 2 data-taking period (2015–2018), the LHC achieved an instantaneous luminosity of twice its design value, resulting in larger background rates and making the efficient detection of muons more difficult. While some backgrounds result from natural radioactivity, cosmic rays, and interactions of the circulating protons with residual gas in the beam pipe, the dominant source of background hits in the muon system arises from proton–proton interactions themselves. Charged hadrons leaving the calorimeters produce energy deposits in the muon chambers. In addition, high-energy particles interacting in the hadron calorimeter and forward shielding elements generate thermal neutrons, which leak out of the calorimeter and shielding structures, filling the CMS cavern. We describe the method used to measure the background rates in the various muon subsystems. These rates, in conjunction with simulations, can be used to estimate the expected backgrounds in the High-Luminosity LHC. This machine will run for at least 10 years starting in 2029 reaching an instantaneous luminosity of 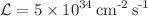 and increasing ultimately to
and increasing ultimately to 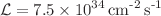 . These background estimates have been a key ingredient for the planning and design of the muon detector upgrade.
. These background estimates have been a key ingredient for the planning and design of the muon detector upgrade.
A. Benvenuti, A. Vorobyev: Deceased.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




