https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-024-13204-8
Regular Article – Theoretical Physics
Dynamics and collision of particles in modified black-bounce geometry
1
Samarkand State University, University Avenue 15, 140104, Samarkand, Uzbekistan
2
School of Science, Harbin Institute of Technology, 518055, ShenZhen, China
3
College of Mathematics and Statistics, Shenzhen University, 518060, Shenzhen, China
4
College of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, 518060, Shenzhen, China
5
Institute of Fundamental and Applied Research, National Research University TIIAME, Kori Niyoziy 39, 100000, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
6
Faculty of Computer Engineering, University of Tashkent for Applied Sciences, Gavhar Str. 1, 700127, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
7
Tashkent State Technical University, 100095, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
8
Ulugh Beg Astronomical Institute, Astronomy Str. 33, 100052, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
9
Shahrisabz State Pedagogical Institute, Shahrisabz Str. 10, 181301, Shahrisabz, Uzbekistan
Received:
3
July
2024
Accepted:
2
August
2024
Published online:
19
August
2024
In the present work, we first regularize a black hole spacetime in modified gravity (MOG) in the presence of the scalar-tensor-vector (STV) field, called the Schwarzschild MOG black hole, under the transformation 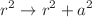 , known as the Simpson–Visser (SV) spacetime (where a is regularization or black-bounce parameter). The spacetime can represent a black hole and a wormhole. We analyze horizon properties and calculate the effective mass of the spacetime. Also, we find black hole-wormhole regions in black-bounce and MOG parameter spacetime. We also analyze scalar invariants of spacetime, such as the Ricci scalar, the square of the Ricci tensor, and the Kretchmann scalar. We study test particle motion in the SV-MOG spacetime by considering the interaction between the particle and the STV field. We investigate how the STV fields change the innermost stable circular orbits (ISCOs), energy, and angular momentum of the test particle’s ISCO. It is shown that the ISCO decreases in the presence of the black bounce parameter and increases in the STV field. We also study the collisions of test particles and analyze how the MOG and black-bounce parameters influence the critical angular momentum of colliding particles and their center of mass energy.
, known as the Simpson–Visser (SV) spacetime (where a is regularization or black-bounce parameter). The spacetime can represent a black hole and a wormhole. We analyze horizon properties and calculate the effective mass of the spacetime. Also, we find black hole-wormhole regions in black-bounce and MOG parameter spacetime. We also analyze scalar invariants of spacetime, such as the Ricci scalar, the square of the Ricci tensor, and the Kretchmann scalar. We study test particle motion in the SV-MOG spacetime by considering the interaction between the particle and the STV field. We investigate how the STV fields change the innermost stable circular orbits (ISCOs), energy, and angular momentum of the test particle’s ISCO. It is shown that the ISCO decreases in the presence of the black bounce parameter and increases in the STV field. We also study the collisions of test particles and analyze how the MOG and black-bounce parameters influence the critical angular momentum of colliding particles and their center of mass energy.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




