https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-024-13178-7
Regular Article – Theoretical Physics
Constraining the EdGB theory with extreme mass-ratio inspirals
1
MOE Key Laboratory of TianQin Mission, TianQin Research Center for Gravitational Physics and School of Physics and Astronomy, Frontiers Science Center for TianQin, CNSA Research Center for Gravitational Waves, Sun Yat-sen University (Zhuhai Campus), 519082, Zhuhai, China
2
Hebei Key Laboratory of High-precision Computation and Application of Quantum Field Theory & Hebei Research Center of the Basic Discipline for Computational Physics & Department of Physics, Hebei University, 071002, Baoding, China
Received:
4
April
2024
Accepted:
30
July
2024
Published online:
17
August
2024
The Einstein-dilaton-Gauss–Bonnet (EdGB) theory is a modified theory of gravity which include a scalar field to couple with the higher order curvature terms. It has already been constrained with various observations include the gravitational wave (GW) with LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA (LVK) Collaboration. In this work, we study the capability for space-borne GW detectors to constrain the EdGB theory using the signal of Extreme Mass-Ratio Inspiral (EMRIs). We use the “numerical kludge (NK)” method to construct the waveform of EMRI in the EdGB theory, focusing on the case when the central black hole is spinless. We then study how a future space-borne gravitational wave detector, TianQin, for example, can place constraints on the EdGB theory through the detection of EMRIs. With the analysis using mismatch and Fisher Information Matrix (FIM), we find that the EdGB parameter 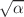 is expected to be constrained to the level of
is expected to be constrained to the level of 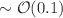 km.
km.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




