https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-024-12834-2
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Search for baryon junctions in photonuclear processes and isobar collisions at RHIC
1
Physics Department, Brookhaven National Laboratory, 11973, Upton, NY, USA
2
State Key Laboratory of Particle Detection and Electronics, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026, Hefei, Anhui, China
3
Department of Physics, East Carolina University, 27858, Greenville, NC, USA
4
Department of Physics, Kent State University, 44242, Kent, OH, USA
5
Physics Department, Ohio State University, 43210, Columbus, Ohio, USA
Received:
3
November
2023
Accepted:
20
April
2024
Published online:
10
June
2024
During the early development of quantum chromodynamics, it was proposed that baryon number could be carried by a non-perturbative Y-shaped topology of gluon fields, called the gluon junction, rather than by the valence quarks as in the QCD standard model. A puzzling feature of ultra-relativistic nucleus-nucleus collisions is the apparent substantial baryon excess in the mid-rapidity region that could not be adequately accounted for in most conventional models of quark and diquark transport. The transport of baryonic gluon junctions is predicted to lead to a characteristic exponential distribution of net-baryon density with rapidity and could resolve the puzzle. In this context we point out that the rapidity density of net-baryons near mid-rapidity indeed follows an exponential distribution with a slope of 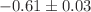 as a function of beam rapidity in the existing global data from A+A collisions at AGS, SPS and RHIC energies. To further test if quarks or gluon junctions carry the baryon quantum number, we propose to study the absolute magnitude of the baryon vs. charge stopping in isobar collisions at RHIC. We also argue that semi-inclusive photon-induced processes (
as a function of beam rapidity in the existing global data from A+A collisions at AGS, SPS and RHIC energies. To further test if quarks or gluon junctions carry the baryon quantum number, we propose to study the absolute magnitude of the baryon vs. charge stopping in isobar collisions at RHIC. We also argue that semi-inclusive photon-induced processes (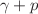 /A) at RHIC kinematics provide an opportunity to search for the signatures of the baryon junction and to shed light onto the mechanisms of observed baryon excess in the mid-rapidity region in ultra-relativistic nucleus-nucleus collisions. Such measurements can be further validated in A+A collisions at the LHC and
/A) at RHIC kinematics provide an opportunity to search for the signatures of the baryon junction and to shed light onto the mechanisms of observed baryon excess in the mid-rapidity region in ultra-relativistic nucleus-nucleus collisions. Such measurements can be further validated in A+A collisions at the LHC and 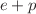 /A collisions at the EIC.
/A collisions at the EIC.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




