https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-024-12445-x
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
The equivalence principle for a plane gravitational wave in torsion-based and non-metricity-based teleparallel equivalents of general relativity
1
Kazan Federal University, Kremlevskaya 18, 420008, Kazan, Russia
2
Sternberg Astronomical Institute, MV Lomonosov State University, Universitetskii pr., 13, 119992, Moscow, Russia
Received:
31
October
2023
Accepted:
11
January
2024
Published online:
1
March
2024
We study the energy–momentum characteristics of the plane “+”-polarized gravitational wave solution of general relativity in the teleparallel equivalent of general relativity (TEGR) and the symmetric teleparallel equivalent of general relativity (STEGR) using the previously constructed Noether currents. The current components describe energy–momentum locally measured by an observer if the displacement vector 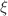 is equal to the observer’s 4-velocity. To determine the non-dynamical connection in these theories, we use the unified “turning off” gravity principle. For a constructive analysis of the values of Noether currents and superpotentials in TEGR and STEGR, we use the concept of “gauges”. The gauge changing can affect the Noether current values. We study under what conditions the Noether current for the freely falling observer is zero. When they are established, the zero result can be interpreted as a correspondence to the equivalence principle, and it is a novelty for gravitational waves in the TEGR and STEGR. We highlight two important cases with positive and zero energy, which reproduce the results of previous works with a different approach for determining gravitational energy–momentum in the TEGR, and give their interpretation.
is equal to the observer’s 4-velocity. To determine the non-dynamical connection in these theories, we use the unified “turning off” gravity principle. For a constructive analysis of the values of Noether currents and superpotentials in TEGR and STEGR, we use the concept of “gauges”. The gauge changing can affect the Noether current values. We study under what conditions the Noether current for the freely falling observer is zero. When they are established, the zero result can be interpreted as a correspondence to the equivalence principle, and it is a novelty for gravitational waves in the TEGR and STEGR. We highlight two important cases with positive and zero energy, which reproduce the results of previous works with a different approach for determining gravitational energy–momentum in the TEGR, and give their interpretation.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




