https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-024-12546-7
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Temporal evolution of cosmological density perturbations of the Bose–Einstein condensate dark matter
Department of Physics, The University of Burdwan, Golapbag, 713104, Purba Bardhaman, West Bengal, India
Received:
31
October
2023
Accepted:
11
February
2024
Published online:
26
February
2024
Dark matter is assumed to be composed of scalar boson particles that form Bose–Einstein condensate during the cosmic evolution of the Universe when the temperature of the dark matter is below the critical temperature 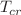 . At around a redshift
. At around a redshift 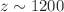 , the normal dark matter converted to Bose–Einstein condensate dark matter through a first-order phase transition and continued to complete the condensation process for nearly
, the normal dark matter converted to Bose–Einstein condensate dark matter through a first-order phase transition and continued to complete the condensation process for nearly 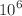 years, until then, both phases coexist. In this manuscript, considering Bose–Einstein condensate dark matter as a Gross–Pitaevskii–Poisson system, we study the time evolution of density contrast of Bose–Einstein condensate dark matter using cosmological linear perturbation theory following previous works on the subject. The evolution equation contains quantum pressure due to Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle and self-interaction pressure terms. We solve the temporal density contrast equation of Bose–Einstein condensate dark matter analytically for both the Thomas-Fermi limit and the non-interacting case where the expansion rule follows similarly to that of the Einstein–de Sitter Universe. In addition, we also numerically analyze the temporal nature of the evolution of density contrast of Bose–Einstein condensate dark matter for the complete equation without applying any approximation. We find that the Bose–Einstein condensate model of dark matter could modify the temporal nature of density contrast evolution due to the presence of self-interaction and quantum pressure terms, which shows significant differences with respect to the conventional standard cold dark matter, and successfully solves the small-scale problems in the context of cosmological structure formation.
years, until then, both phases coexist. In this manuscript, considering Bose–Einstein condensate dark matter as a Gross–Pitaevskii–Poisson system, we study the time evolution of density contrast of Bose–Einstein condensate dark matter using cosmological linear perturbation theory following previous works on the subject. The evolution equation contains quantum pressure due to Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle and self-interaction pressure terms. We solve the temporal density contrast equation of Bose–Einstein condensate dark matter analytically for both the Thomas-Fermi limit and the non-interacting case where the expansion rule follows similarly to that of the Einstein–de Sitter Universe. In addition, we also numerically analyze the temporal nature of the evolution of density contrast of Bose–Einstein condensate dark matter for the complete equation without applying any approximation. We find that the Bose–Einstein condensate model of dark matter could modify the temporal nature of density contrast evolution due to the presence of self-interaction and quantum pressure terms, which shows significant differences with respect to the conventional standard cold dark matter, and successfully solves the small-scale problems in the context of cosmological structure formation.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.




