https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-024-12437-x
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Cosmological constraints on the 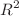 -corrected Appleby–Battye model
-corrected Appleby–Battye model
1
Observatório Nacional, 20921-400, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
2
Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, 27930-560, Macaé, Brazil
Received:
15
September
2023
Accepted:
11
January
2024
Published online:
3
February
2024
Nowadays, efforts are being devoted to the study of alternative cosmological scenarios, in which, modifications of the General Relativity theory have been proposed to explain the late cosmic acceleration without assuming the existence of the dark energy component. In this scenario, we investigate the 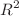 -corrected Appleby–Battye model, or
-corrected Appleby–Battye model, or 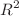 -AB model, which consists of an f(R) model with only one extra free parameter b, besides the cosmological parameters of the flat-
-AB model, which consists of an f(R) model with only one extra free parameter b, besides the cosmological parameters of the flat-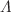 CDM model:
CDM model: 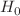 and
and  . Regarding this model, it was already shown that a positive value for b is required for the model to be consistent with Solar System tests, moreover, the condition for the existence of a de Sitter state requires
. Regarding this model, it was already shown that a positive value for b is required for the model to be consistent with Solar System tests, moreover, the condition for the existence of a de Sitter state requires  . To impose observational constraints on the
. To impose observational constraints on the 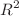 -AB model we consider three datasets: 31 H(z) measurements from Cosmic Chronometers (CC), 20
-AB model we consider three datasets: 31 H(z) measurements from Cosmic Chronometers (CC), 20 $$](/articles/epjc/abs/2024/02/10052_2024_Article_12437/10052_2024_Article_12437_tex_eq10.png) measurements from Redshift-Space Distortion (RSD), and the most recent type Ia Supernovae (SNe Ia) sample from Pantheon+. Next, we perform two diferent analyses: we have cosidered only SNe Ia data and the combined likelihood SNe
measurements from Redshift-Space Distortion (RSD), and the most recent type Ia Supernovae (SNe Ia) sample from Pantheon+. Next, we perform two diferent analyses: we have cosidered only SNe Ia data and the combined likelihood SNe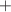 CC
CC RSD. The first one has provided
RSD. The first one has provided 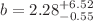 , while the second one
, while the second one  . In the first case it was necessary to set the absolute magnitude
. In the first case it was necessary to set the absolute magnitude  from SH0ES collaboration, while in the second we did a marginalization over the Hubble constant
from SH0ES collaboration, while in the second we did a marginalization over the Hubble constant 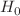 in the normalized growth function. We have also observed that the
in the normalized growth function. We have also observed that the  degenerecency was broken by adding CC data to the SNe data. Additionally, we perform illustrative analyses that compare this f(R) model with the flat-
degenerecency was broken by adding CC data to the SNe data. Additionally, we perform illustrative analyses that compare this f(R) model with the flat-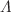 CDM model, considering several values of the parameter b, for diverse cosmological functions like the Hubble function H(z), the equation of state
CDM model, considering several values of the parameter b, for diverse cosmological functions like the Hubble function H(z), the equation of state 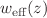 , the parametrized growth rate of cosmic structures
, the parametrized growth rate of cosmic structures $$](/articles/epjc/abs/2024/02/10052_2024_Article_12437/10052_2024_Article_12437_tex_eq20.png) , and
, and  . From our results, we conclude that the
. From our results, we conclude that the 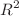 -AB model fits well current observational data, although the model parameter b was not unambiguously constrained in the analyses.
-AB model fits well current observational data, although the model parameter b was not unambiguously constrained in the analyses.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




