https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-024-12434-0
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Synchronize your chrono-brane: testing a variable brane tension model with strong gravitational lensing
1
Instituto de Astronomía, Observatorio Astronómico Nacional, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Apartado postal 106, C.P. 22800, Ensenada, Mexico
2
Unidad Académica de Física Universidad Autónoma de Zacatecas, Calzada Solidaridad esquina con Paseo a la Bufa S/Nt, C.P. 98060, Zacatecas, Mexico
3
Escuela de Ingeniería, Universidad Central de Chile, Avenida Francisco de Aguirre 0405, 171-0164, La Serena, Coquimbo, Chile
4
Depto. de Física y Matemáticas, Universidad Iberoamericana Ciudad de México, Prolongación Paseo de la Reforma 880, 01219, Mexico, Mexico
5
Facultad de Ingeniería, Universidad Autónoma de Querétaro, Centro Universitario Cerro de las Campanas, 76010, Santiago de Querétaro, Mexico
6
Instituto de Física y Astronomía, Universidad de Valparaíso, Avda. Gran Bretaña, 1111, Valparaíso, Chile
Received:
25
June
2023
Accepted:
11
January
2024
Published online:
29
January
2024
Brane world models have shown to be promising to understand the late cosmic acceleration, in particular because such acceleration can be naturally derived, mimicking the dark energy behaviour just with a five dimensional geometry. In this paper we present a strong lensing joint analysis using a compilation of early-type galaxies acting as a lenses, united with the power of the well studied strong lensing galaxy cluster Abell 1689. We use the strong lensing constraints to investigate a brane model with variable brane tension as a function of the redshift. In our joint analysis we found a value  , for the exponent related to the brane tension, showing that n deviates from a Cosmological Constant (CC) scenario (n=6). We obtain a value for the deceleration parameter, q(z) today,
, for the exponent related to the brane tension, showing that n deviates from a Cosmological Constant (CC) scenario (n=6). We obtain a value for the deceleration parameter, q(z) today,  , and a transition redshift,
, and a transition redshift, 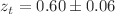 (when the Universe change from an decelerated phase to an accelerated one). These results are in contrast with previous work that favors CC scenario, nevertheless our lensing analysis is in agreement with a formerly reported conclusion suggesting that the variable brane tension model is able to source a late cosmic acceleration without an extra fluid as in the standard one.
(when the Universe change from an decelerated phase to an accelerated one). These results are in contrast with previous work that favors CC scenario, nevertheless our lensing analysis is in agreement with a formerly reported conclusion suggesting that the variable brane tension model is able to source a late cosmic acceleration without an extra fluid as in the standard one.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3. SCOAP3 supports the goals of the International Year of Basic Sciences for Sustainable Development.




