https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-023-12312-1
Regular Article - Experimental Physics
Constraints on directionality effect of nuclear recoils in a liquid argon time projection chamber
1
Gran Sasso Science Institute, 67100, L’Aquila, Italy
2
AstroCeNT, Nicolaus Copernicus Astronomical Center of the Polish Academy of Sciences, 00-614, Warsaw, Poland
3
INFN Catania, 95121, Catania, Italy
4
Università of Catania, 95124, Catania, Italy
5
Instituto de Física, Universidade de São Paulo, 05508-090, São Paulo, Brazil
6
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, 99352, Richland, WA, USA
7
Physics Department, Augustana University, 57197, Sioux Falls, SD, USA
8
TRIUMF, 4004 Wesbrook Mall, V6T 2A3, Vancouver, BC, Canada
9
INFN Cagliari, 09042, Cagliari, Italy
10
Mendeleev University of Chemical Technology, 125047, Moscow, Russia
11
INFN Laboratori Nazionali di Legnaro, 35020, Legnaro, Padua, Italy
12
Department of Physics, Royal Holloway University of London, TW20 0EX, Egham, UK
13
CIEMAT, Centro de Investigaciones Energéticas, Medioambientales y Tecnológicas, 28040, Madrid, Spain
14
Centre de Physique des Particules de Marseille, Aix Marseille Univ, CNRS/IN2P3, CPPM, Marseille, France
15
INFN Napoli, 80126, Naples, Italy
16
INFN Pisa, 56127, Pisa, Italy
17
Physics Department, Università degli Studi di Pisa, 56127, Pisa, Italy
18
INFN Sezione di Roma, 00185, Rome, Italy
19
Physics Department, Università degli Studi di Genova, 16146, Genoa, Italy
20
INFN Genova, 16146, Genoa, Italy
21
Physics Department, Princeton University, 08544, Princeton, NJ, USA
22
Department of Physics, Carleton University, K1S 5B6, Ottawa, ON, Canada
23
Physics Department, Università degli Studi di Cagliari, 09042, Cagliari, Italy
24
INFN Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso, 67100, Assergi, AQ, Italy
25
Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Università degli Studi di Cagliari, 09123, Cagliari, Italy
26
Physics Department, Università degli Studi “Federico II” di Napoli, 80126, Naples, Italy
27
Centro de Astropartículas y Física de Altas Energías, Universidad de Zaragoza, 50009, Zaragoza, Spain
28
Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics, Lomonosov Moscow State University, 119234, Moscow, Russia
29
Department of Physics and Astronomy, Università degli Studi di Bologna, 40126, Bologna, Italy
30
INFN Bologna, 40126, Bologna, Italy
31
INFN Milano, 20133, Milan, Italy
32
SNOLAB, P3Y 1N2, Lively, ON, Canada
33
Department of Physics and Astronomy, Laurentian University, P3E 2C6, ON, Sudbury, Canada
34
M. Smoluchowski Institute of Physics, Jagiellonian University, 30-348, Kraków, Poland
35
Department of Strutture per l’Ingegneria e l’Architettura, Università degli Studi “Federico II” di Napoli, 80131, Naples, Italy
36
INFN Torino, 10125, Turin, Italy
37
Physics Department, Sapienza Università di Roma, 00185, Rome, Italy
38
Physics Department, Università degli Studi di Salerno, 84084, Salerno, Italy
39
INFN Salerno, 84084, Salerno, Italy
40
Chemistry, Physics, Mathematics and Natural Sciences Department, Università di Sassari, 07100, Sassari, Italy
41
Saint Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute, 188350, Gatchina, Russia
42
Department of Physics, Engineering Physics and Astronomy, Queen’s University, K7L 3N6, Kingston, ON, Canada
43
National Research Centre Kurchatov Institute, 123182, Moscow, Russia
44
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, 95616, Davis, CA, USA
45
Physics Department, Lancaster University, LA1 4YB, Lancaster, UK
46
APC, Université de Paris, CNRS, Astroparticule et Cosmologie, 75013, Paris, France
47
Museo Storico della Fisica e Centro Studi e Ricerche Enrico Fermi, 00184, Rome, Italy
48
Institute for Particle Physics, ETH Zürich, 8093, Zurich, Switzerland
49
LPNHE, CNRS/IN2P3, Sorbonne Université, Université Paris Diderot, 75252, Paris, France
50
Williams College, Physics Department, 01267, Williamstown, MA, USA
51
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Hawai’i, 96822, Honolulu, HI, USA
52
Fondazione Bruno Kessler, 38123, Povo, Italy
53
Trento Institute for Fundamental Physics and Applications, 38123, Povo, Italy
54
National Research Nuclear University MEPhI, 115409, Moscow, Russia
55
Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, 141980, Dubna, Russia
56
Institute of High Energy Physics, 100049, Beijing, China
57
Engineering and Architecture Faculty, Università di Enna Kore, 94100, Enna, Italy
58
INFN Laboratori Nazionali del Sud, 95123, Catania, Italy
59
Department of Physics, University of Alberta, T6G 2R3, Edmonton, AB, Canada
60
School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Edinburgh, EH9 3FD, Edinburgh, UK
61
Università degli Studi dell’Aquila, 67100, L’Aquila, Italy
62
Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, 60510, Batavia, IL, USA
63
Radiation Physics Laboratory, Belgorod National Research University, 308007, Belgorod, Russia
64
Pharmacy Department, Università degli Studi “Federico II” di Napoli, 80131, Naples, Italy
65
School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Birmingham, Edgbaston, B15 2TT, Birmingham, UK
66
INFN Roma Tre, 00146, Rome, Italy
67
Mathematics and Physics Department, Università degli Studi Roma Tre, 00146, Rome, Italy
68
Virginia Tech, 24061, Blacksburg, VA, USA
69
Fundación ARAID, Universidad de Zaragoza, 50009, Zaragoza, Spain
70
Physics Department, Temple University, 19122, Philadelphia, PA, USA
71
Department of Physics, University of Liverpool, The Oliver Lodge Laboratory, L69 7ZE, Liverpool, UK
72
Department of Physics, University of Warwick, CV47AL, Coventry, UK
73
Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, 630090, Novosibirsk, Russia
74
Novosibirsk State University, 630090, Novosibirsk, Russia
75
Amherst Center for Fundamental Interactions and Physics Department, University of Massachusetts, 01003, Amherst, MA, USA
76
Department of Physics and Astronomy, The University of Manchester, M13 9PL, Manchester, UK
77
Physics Department, Università degli Studi di Milano, 20133, Milan, Italy
78
Department of Physics, University of Houston, 77204, Houston, TX, USA
79
Chemical, Materials, and Industrial Production Engineering Department, Università degli Studi “Federico II” di Napoli, 80126, Naples, Italy
80
Department of Electronics and Communications, Politecnico di Torino, 10129, Turin, Italy
81
Physics and Astronomy Department, University of California, 90095, Los Angeles, CA, USA
82
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100049, Beijing, China
83
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, 92507, Riverside, CA, USA
84
Department of Physics and Engineering, Fort Lewis College, 81301, Durango, CO, USA
85
INFN, Rome, Italy
Received:
28
July
2023
Accepted:
30
November
2023
Published online:
10
January
2024
The direct search for dark matter in the form of weakly interacting massive particles (WIMP) is performed by detecting nuclear recoils produced in a target material from the WIMP elastic scattering. The experimental identification of the direction of the WIMP-induced nuclear recoils is a crucial asset in this field, as it enables unmistakable modulation signatures for dark matter. The Recoil Directionality (ReD) experiment was designed to probe for such directional sensitivity in argon dual-phase time projection chambers (TPC), that are widely considered for current and future direct dark matter searches. The TPC of ReD was irradiated with neutrons at the INFN Laboratori Nazionali del Sud. Data were taken with nuclear recoils of known directions and kinetic energy of 72 keV, which is within the range of interest for WIMP-induced signals in argon. The direction-dependent liquid argon charge recombination model by Cataudella et al. was adopted and a likelihood statistical analysis was performed, which gave no indications of significant dependence of the detector response to the recoil direction. The aspect ratio R of the initial ionization cloud is 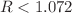 with 90 % confidence level.
with 90 % confidence level.
G. Cappello, V. Cataudella, A. de Candia, G. De Filippis, D. Dell’Aquila, C. Dionisi, N. Kemmerich, X. Li, A. Sosa: Not a member of the DarkSide-20k Collaboration.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3. SCOAP3 supports the goals of the International Year of Basic Sciences for Sustainable Development.




