https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-023-12172-9
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
On the Kalb–Ramond modified Lorentz violating hairy black holes and Thorne’s hoop conjecture
1
Zel’dovich International Center for Astrophysics, M. Akmullah Bashkir State Pedagogical University, 3A, October Revolution Street, 450008, Ufa, RB, Russia
2
High Energy Cosmic Ray Research Center, University of North Bengal, 734013, Siliguri, WB, India
3
Ufa University of Science and Technology, Sterlitamak Campus, Lenin Avenue, 49, 453103, Sterlitamak, RB, Russia
Received:
17
August
2023
Accepted:
19
October
2023
Published online:
31
October
2023
Recently, a class of static spherically symmetric power law corrected Lorentz violating (LV) Schwarzschild black holes in the Kalb–Ramond model have been derived and studied in the specific range of LV parameters (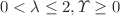 ) that correspond to energy condition preserving (
) that correspond to energy condition preserving (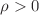 ) source. On the other hand, there exist well known black holes that do not preserve the energy conditions. In this paper, we shall therefore relax energy conditions and numerically explore the horizon patterns of the enlarged class of LSMA black holes. Four generic types of LV corrected black holes emerge, which interestingly include the analogue of the braneworld black hole (
) source. On the other hand, there exist well known black holes that do not preserve the energy conditions. In this paper, we shall therefore relax energy conditions and numerically explore the horizon patterns of the enlarged class of LSMA black holes. Four generic types of LV corrected black holes emerge, which interestingly include the analogue of the braneworld black hole (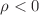 ) lending to
) lending to  a new interpretation of “tidal charge” known as an imprint from the 5d bulk in the Randall–Sundrum scenario. We shall then show that Thorne’s hoop conjecture,
a new interpretation of “tidal charge” known as an imprint from the 5d bulk in the Randall–Sundrum scenario. We shall then show that Thorne’s hoop conjecture, 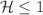 , where
, where 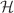 is the Hod function, consistently holds for three types and their generalizations. However, intriguingly, it turns out that, for the remaining type (viz., Schwarzschild–de Sitter and its generalizations), the hoop conjecture does not hold. It is also shown that braneworld tidal charge black holes increases the LV correction to planetary perihelion advance in contrast to the decrease due to ordinary black holes thereby providing a qualitative distinction between them.
is the Hod function, consistently holds for three types and their generalizations. However, intriguingly, it turns out that, for the remaining type (viz., Schwarzschild–de Sitter and its generalizations), the hoop conjecture does not hold. It is also shown that braneworld tidal charge black holes increases the LV correction to planetary perihelion advance in contrast to the decrease due to ordinary black holes thereby providing a qualitative distinction between them.
K. K. Nandi, R. N. Izmailov, R. Kh. Karimov and A. A. Potapov contributed equally to this work.
© The Author(s) 2023
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3. SCOAP3 supports the goals of the International Year of Basic Sciences for Sustainable Development.




