https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-023-12122-5
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Matter growth perturbations and cosmography in modified torsion cosmology
1
Department of Mathematics, COMSATS University, Islamabad, Lahore-Campus, 54000, Lahore, Pakistan
2
Department of Natural Sciences and Humanities, University of Engineering and Technology, Lahore, New Campus, KSK, Pakistan
3
Institute for Theoretical Physics and Cosmology, Zhejiang University of Technology, 310023, Hangzhou, China
b jawadab181@yahoo.com, abduljawad@cuilahore.edu.pk
Received:
31
July
2023
Accepted:
5
October
2023
Published online:
24
October
2023
We examine the cosmic evolution of the growth of perturbations with respect to matter content at early and recent past era of the Universe under the framework of non-zero torsion cosmology. Some cosmographic parameters are also discussed. To analyze this cosmic scenario, we formulate the cosmic models with two dark matter considerations and apply spherical collapse formalism. We explore that for model-1 (pressureless matter), the density contrast starts growing in early era of the Universe and with the Universe’s overall expansion, density contrast grows faster for different choices of torsion parameter. In model-2 (matter with non-zero pressure), the density contrast shows enormous growth as compared to overall expansion of the Universe for the perturbed region, which indicates the collapse of the perturbed region and formulation of new large scale matter or galaxy. Further, we analyze the behavior of the growth function for both models with different values of torsion parameter. For model-1, the growth function increases smoothly for different choices of torsion parameter but for the model-2 the behavior of the growth function with nonzero DM and torsion significantly deviates from pressureless DM with zero torsion (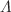 CDM). We also investigate different cosmographic parameters for both models and analyze their behavior with different choices of torsion parameter and
CDM). We also investigate different cosmographic parameters for both models and analyze their behavior with different choices of torsion parameter and 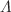 CDM. The results show the power-law expansion rate of the accelerating Universe with respect to redshift function.
CDM. The results show the power-law expansion rate of the accelerating Universe with respect to redshift function.
© The Author(s) 2023
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3. SCOAP3 supports the goals of the International Year of Basic Sciences for Sustainable Development.




