https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-022-10715-0
Letter
Back-to-back azimuthal correlations in  jet events at high transverse momentum in the TMD parton branching method at next-to-leading order
jet events at high transverse momentum in the TMD parton branching method at next-to-leading order
1
School of Physics, Peking University, Beijing, China
2
Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESY, Hamburg, Germany
3
Theoretical Physics Department, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland
4
Elementary Particle Physics, University of Antwerp, Antwerp, Belgium
5
University of Oxford, Oxford, UK
6
University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
7
Department of Astronomy and Theoretical Physics, Lund University, Lund, Sweden
Received:
7
April
2022
Accepted:
16
August
2022
Published online:
29
August
2022
Azimuthal correlations in  jet production at large transverse momenta are computed by matching Parton-Branching (PB) TMD parton distributions and showers with NLO calculations via MCatNLO. The predictions are compared with those for dijet production in the same kinematic range. The azimuthal correlations
jet production at large transverse momenta are computed by matching Parton-Branching (PB) TMD parton distributions and showers with NLO calculations via MCatNLO. The predictions are compared with those for dijet production in the same kinematic range. The azimuthal correlations 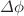 between the Z boson and the leading jet are steeper compared to those in dijet production at transverse momenta
between the Z boson and the leading jet are steeper compared to those in dijet production at transverse momenta 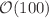 GeV , while they become similar for very high transverse momenta
GeV , while they become similar for very high transverse momenta 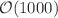 GeV . The different patterns of
GeV . The different patterns of  jet and dijet azimuthal correlations can be used to search for potential factorization-breaking effects in the back-to-back region, which depend on the different color and spin structure of the final states and their interferences with the initial states. In order to investigate these effects experimentally, we propose to measure the ratio of the distributions in
jet and dijet azimuthal correlations can be used to search for potential factorization-breaking effects in the back-to-back region, which depend on the different color and spin structure of the final states and their interferences with the initial states. In order to investigate these effects experimentally, we propose to measure the ratio of the distributions in 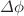 for
for  jet- and multijet production at low and at high transverse momenta, and compare the results to predictions obtained assuming factorization. We examine the role of theoretical uncertainties by performing variations of the factorization scale, renormalization scale and matching scale. In particular, we present a comparative study of matching scale uncertainties in the cases of PB-TMD and collinear parton showers.
jet- and multijet production at low and at high transverse momenta, and compare the results to predictions obtained assuming factorization. We examine the role of theoretical uncertainties by performing variations of the factorization scale, renormalization scale and matching scale. In particular, we present a comparative study of matching scale uncertainties in the cases of PB-TMD and collinear parton showers.
© The Author(s) 2022
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3. SCOAP3 supports the goals of the International Year of Basic Sciences for Sustainable Development.




