https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-022-10501-y
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Cosmogenic background study for a 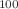 Mo-based bolometric demonstration experiment at China JinPing underground Laboratory
Mo-based bolometric demonstration experiment at China JinPing underground Laboratory
1
Key Laboratory of Nuclear Physics and Ion-beam Application (MOE), Institute of Modern Physics, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
2
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA
Received:
19
January
2022
Accepted:
7
June
2022
Published online:
22
June
2022
We perform simulation study for a 10-kg 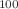 Mo-based bolometeric demonstration experiment for neutrinoless double-beta decay (
Mo-based bolometeric demonstration experiment for neutrinoless double-beta decay ( ) search at China JinPing underground Laboratory (CJPL). Cosmogenic production of radionuclides in
) search at China JinPing underground Laboratory (CJPL). Cosmogenic production of radionuclides in 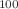 Mo-enriched lithium molybdate crystals and copper components of the detector system are studied using Geant4 toolkit based on the simulated cosmic ray data from the CRY library. Background energy spectra of the cosmogenic radionuclides including
Mo-enriched lithium molybdate crystals and copper components of the detector system are studied using Geant4 toolkit based on the simulated cosmic ray data from the CRY library. Background energy spectra of the cosmogenic radionuclides including  Co,
Co,  Rb and
Rb and  Y which are harmful for the
Y which are harmful for the 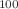 Mo-based
Mo-based  experiment are investigated. We then evaluate the total cosmogenic background level in the
experiment are investigated. We then evaluate the total cosmogenic background level in the 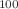 Mo
Mo  search energy region of interest (ROI) for the demonstration experiment. After one year of cooling down underground, the residual background contribution is found to be 1.8
search energy region of interest (ROI) for the demonstration experiment. After one year of cooling down underground, the residual background contribution is found to be 1.8  10
10 cts/kg/keV/yr and 3.3
cts/kg/keV/yr and 3.3 10
10 cts/kg/keV/yr from crystals and copper components, respectively. Furthermore, underground cosmogenic activation of copper and lithium molybdate crystal is calculated based on the simulation spectra of neutron and proton in CJPL. The underground cosmogenic background is found to be negligible in the ROI.
cts/kg/keV/yr from crystals and copper components, respectively. Furthermore, underground cosmogenic activation of copper and lithium molybdate crystal is calculated based on the simulation spectra of neutron and proton in CJPL. The underground cosmogenic background is found to be negligible in the ROI.
© The Author(s) 2022
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3




