https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-022-10243-x
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Residual mean field model of valence quarks in the nucleon
Department of Physics, Florida International University, 33199, Miami, FL, USA
Received:
6
December
2021
Accepted:
23
March
2022
Published online:
8
April
2022
We develop a non-perturbative model for valence parton distribution functions (PDFs) based on the mean field interactions of valence quarks in the nucleonic interior. The main motivation for the model is to obtain a mean field description of the valence quarks as a baseline to study the short range quark–quark interactions that generate the high x tail of PDFs. The model is based on the separation of the valence three-quark cluster and residual system in the nucleon. Then the nucleon structure function is calculated within the effective light-front diagrammatic approach introducing nonperturbative light-front valence quark and residual wave functions. Within the model a new relation is obtained between the position, 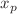 , of the peak of
, of the peak of 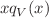 distribution of the valence quark and the effective mass of the residual system,
distribution of the valence quark and the effective mass of the residual system, 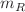 , in the form:
, in the form: 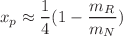 at starting
at starting 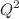 . This relation explains the difference in the peak positions for d- and u-quarks through the expected difference of residual masses for valence d- and u-quark distributions. The parameters of the model are fixed by fitting the calculated valence quark distributions to the phenomenological PDFs. This allowed us to estimate the overall mean field contribution in baryonic and momentum sum rules for valence d- and u-quarks. Finally, the evaluated parameters of the non-perturbative wave functions of valence 3q-cluster and residual system can be used in calculation of other quantities such as nucleon form factors, generalized partonic and transverse momentum distributions.
. This relation explains the difference in the peak positions for d- and u-quarks through the expected difference of residual masses for valence d- and u-quark distributions. The parameters of the model are fixed by fitting the calculated valence quark distributions to the phenomenological PDFs. This allowed us to estimate the overall mean field contribution in baryonic and momentum sum rules for valence d- and u-quarks. Finally, the evaluated parameters of the non-perturbative wave functions of valence 3q-cluster and residual system can be used in calculation of other quantities such as nucleon form factors, generalized partonic and transverse momentum distributions.
© The Author(s) 2022
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3




