https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-022-10034-4
Regular Article - Experimental Physics
Reconstructing the neutrino energy for in-ice radio detectors
A study for the Radio Neutrino Observatory Greenland (RNO-G)
1
Science Faculty CP230, Université Libre de Bruxelles, 1050, Brussels, Belgium
2
Department of Physics, Center for Cosmology and AstroParticle Physics, Ohio State University, 43210, Columbus, OH, USA
3
Division of Electricity, Department of Engineering Sciences, Uppsala University, 752 37, Uppsala, Sweden
4
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Kansas, 66045, Lawrence, KS, USA
5
National Nuclear Research University MEPhI, Kashirskoe Shosse 31, 115409, Moscow, Russia
6
Department of Physics and Astronomy, Uppsala University, 752 37, Uppsala, Sweden
7
Astrophysical Institute, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Pleinlaan 2, 1050, Brussels, Belgium
8
Physics Department, California Polytechnic State University, 93407, San Luis Obispo, CA, USA
9
Department of Physics and Astronomy, Michigan State University, 48824, East Lansing, MI, USA
10
Dienst ELEM, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, 1050, Brussels, Belgium
11
Department of Physics, Enrico Fermi Inst., Kavli Inst. for Cosmological Physics, University of Chicago, 60637, Chicago, IL, USA
12
Wisconsin IceCube Particle Astrophysics Center (WIPAC) and Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, 53703, Madison, WI, USA
13
Erlangen Center for Astroparticle Physics (ECAP), Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-Nuremberg, 91058, Erlangen, Germany
14
DESY, Platanenallee 6, 15738, Zeuthen, Germany
15
Whittier College, 90602, Whittier, CA, USA
16
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, 94720, Berkeley, CA, USA
17
Department of Physics, Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Penn State University, 16801, University Park, PA, USA
18
Department of Physics and Astronomy, Ghent University, 9000, Gent, Belgium
19
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, 19716, Newark, DE, USA
20
KVI-Center for Advanced Radiation Technology, University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands
bj authors@rno-g.org, christoph.welling@desy.de
Received:
7
July
2021
Accepted:
17
January
2022
Published online:
16
February
2022
Since summer 2021, the Radio Neutrino Observatory in Greenland (RNO-G) is searching for astrophysical neutrinos at energies 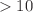 PeV by detecting the radio emission from particle showers in the ice around Summit Station, Greenland. We present an extensive simulation study that shows how RNO-G will be able to measure the energy of such particle cascades, which will in turn be used to estimate the energy of the incoming neutrino that caused them. The location of the neutrino interaction is determined using the differences in arrival times between channels and the electric field of the radio signal is reconstructed using a novel approach based on Information Field Theory. Based on these properties, the shower energy can be estimated. We show that this method can achieve an uncertainty of 13% on the logarithm of the shower energy after modest quality cuts and estimate how this can constrain the energy of the neutrino. The method presented in this paper is applicable to all similar radio neutrino detectors, such as the proposed radio array of IceCube-Gen2.
PeV by detecting the radio emission from particle showers in the ice around Summit Station, Greenland. We present an extensive simulation study that shows how RNO-G will be able to measure the energy of such particle cascades, which will in turn be used to estimate the energy of the incoming neutrino that caused them. The location of the neutrino interaction is determined using the differences in arrival times between channels and the electric field of the radio signal is reconstructed using a novel approach based on Information Field Theory. Based on these properties, the shower energy can be estimated. We show that this method can achieve an uncertainty of 13% on the logarithm of the shower energy after modest quality cuts and estimate how this can constrain the energy of the neutrino. The method presented in this paper is applicable to all similar radio neutrino detectors, such as the proposed radio array of IceCube-Gen2.
© The Author(s) 2022
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3




