https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-021-09965-1
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Magnetized Einstein–Maxwell-dilaton model under an external electric field
School of Physics, Damghan University, 41167-36716, Damghan, Iran
Received:
11
November
2021
Accepted:
21
December
2021
Published online:
13
January
2022
We employ an analytic solution of a magnetized Einstein–Maxwell-dilaton gravity model whose parameters have been determined so that its holographic dual has the most similarity to the confining QCD-like theories. Analyzing the total potential of a quark–antiquark pair, we are able to investigate the effect of an electric field on different phases of the background which are the thermal AdS and black hole phases. This is helpful for better understanding of the confining character and the phases of the system. We find out that the field theory dual to the black hole solution is always deconfined, as expected. However, although the thermal AdS phase generally describes the confining phase, for quark pairs parallel to B (longitudinal case) with 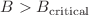 the response of the system mimics the deconfinement, since there is no IR wall in the bulk and the critical field
the response of the system mimics the deconfinement, since there is no IR wall in the bulk and the critical field  , as is the case for the deconfined phase. We moreover observe that in the black hole phase with sufficiently small values of
, as is the case for the deconfined phase. We moreover observe that in the black hole phase with sufficiently small values of 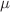 and in the thermal AdS phase, for both longitudinal and transverse cases, the magnetic field enhances the Schwinger effect, which can be termed as the inverse magnetic catalysis (IMC). This is deduced both from the decrease of critical electric fields and decreasing the height and width of the total potential barrier the quarks are facing with. However, by increasing
and in the thermal AdS phase, for both longitudinal and transverse cases, the magnetic field enhances the Schwinger effect, which can be termed as the inverse magnetic catalysis (IMC). This is deduced both from the decrease of critical electric fields and decreasing the height and width of the total potential barrier the quarks are facing with. However, by increasing 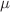 to higher values, IMC turns into magnetic catalysis, as also observed from the diagram of the Hawking–Page phase transition temperature versus B for the background geometry.
to higher values, IMC turns into magnetic catalysis, as also observed from the diagram of the Hawking–Page phase transition temperature versus B for the background geometry.
© The Author(s) 2022
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3




