https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-021-09889-w
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Viscous cosmology in the Weyl-type f(Q, T) gravity
Department of Mathematics, Birla Institute of Technology and Science-Pilani, Hyderabad Campus, 500078, Hyderabad, India
c
pksahoo@hyderabad.bits-pilani.ac.in
Received:
4
October
2021
Accepted:
28
November
2021
Published online:
9
December
2021
Bulk viscosity is the only viscous influence that can change the background dynamics in a homogeneous and isotropic universe. In the present work, we analyze the bulk viscous cosmological model with the bulk viscosity coefficient of the form 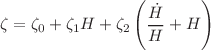 where,
where, 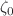 ,
, 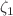 and
and 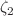 are bulk viscous parameters, and H is the Hubble parameter. We investigate the impact of the bulk viscous parameter on dynamics of the universe in the recently proposed Weyl-type f(Q, T) gravity, where Q is the non-metricity, and T is the trace of the matter energy–momentum tensor. The exact solutions to the corresponding field equations are obtained with the viscous fluid and the linear model of the form
are bulk viscous parameters, and H is the Hubble parameter. We investigate the impact of the bulk viscous parameter on dynamics of the universe in the recently proposed Weyl-type f(Q, T) gravity, where Q is the non-metricity, and T is the trace of the matter energy–momentum tensor. The exact solutions to the corresponding field equations are obtained with the viscous fluid and the linear model of the form 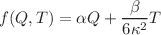 , where
, where 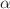 and
and 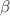 are model parameters. Further, we constrain the model parameters using the 57 points Hubble dataset the recently released 1048 points Pantheon sample and the combination Hz + BAO + Pantheon, which shows our model is good congeniality with observations. We study the possible scenarios and the evolution of the universe through the deceleration parameter, the equation of state (EoS) parameter, the statefinder diagnostics, and the Om diagnostics. It is observed that the universe exhibits a transition from a decelerated to an accelerated phase of the universe under certain constraints of model parameters.
are model parameters. Further, we constrain the model parameters using the 57 points Hubble dataset the recently released 1048 points Pantheon sample and the combination Hz + BAO + Pantheon, which shows our model is good congeniality with observations. We study the possible scenarios and the evolution of the universe through the deceleration parameter, the equation of state (EoS) parameter, the statefinder diagnostics, and the Om diagnostics. It is observed that the universe exhibits a transition from a decelerated to an accelerated phase of the universe under certain constraints of model parameters.
© The Author(s) 2021
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3




