https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-021-09782-6
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Dynamics of charged test particles around quantum-corrected Schwarzschild black holes
1
Purple Mountain Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 210023, Nanjing, China
2
School of Astronomy and Space Science, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026, Hefei, China
Received:
12
March
2021
Accepted:
31
October
2021
Published online:
9
November
2021
We investigate neutral and charged test particles’ motions around quantum-corrected Schwarzschild black holes immersed in an external magnetic field. Taking the innermost stable circular orbits of neutral timelike particles into account, we find that the black holes can mimic different ranges of the Kerr black hole’s spin |a/M| from 0.15 to 0.99. Our analysis of charged test particles’ motions suggests that the values of the angular momentum l and the energy 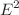 are slightly higher than Schwarzschild black holes. The allowed regions of the
are slightly higher than Schwarzschild black holes. The allowed regions of the 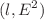 demonstrate that the critical energy
demonstrate that the critical energy 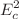 divides the charged test particle’s bounded trajectory into three types. With the help of a Monte Carlo method, we study the charged particles’ probabilities of falling into the black holes and find that the probability density function against l depends on the signs of the particles’ charges. Finally, the epicyclic frequencies of the charged particles are considered with respect to the observed twin peak quasi-periodic oscillations frequencies. Our results might provide hints for distinguishing quantum-corrected Schwarzschild black holes from Schwarzschild ones by using the dynamics of charged test particles around the strong gravitational field.
divides the charged test particle’s bounded trajectory into three types. With the help of a Monte Carlo method, we study the charged particles’ probabilities of falling into the black holes and find that the probability density function against l depends on the signs of the particles’ charges. Finally, the epicyclic frequencies of the charged particles are considered with respect to the observed twin peak quasi-periodic oscillations frequencies. Our results might provide hints for distinguishing quantum-corrected Schwarzschild black holes from Schwarzschild ones by using the dynamics of charged test particles around the strong gravitational field.
© The Author(s) 2021
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3




